417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
有一个 m × n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m x n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。
岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。
返回网格坐标 result 的 2D 列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水从单元格 (ri, ci) 流动 既可流向太平洋也可流向大西洋 。
示例 1:
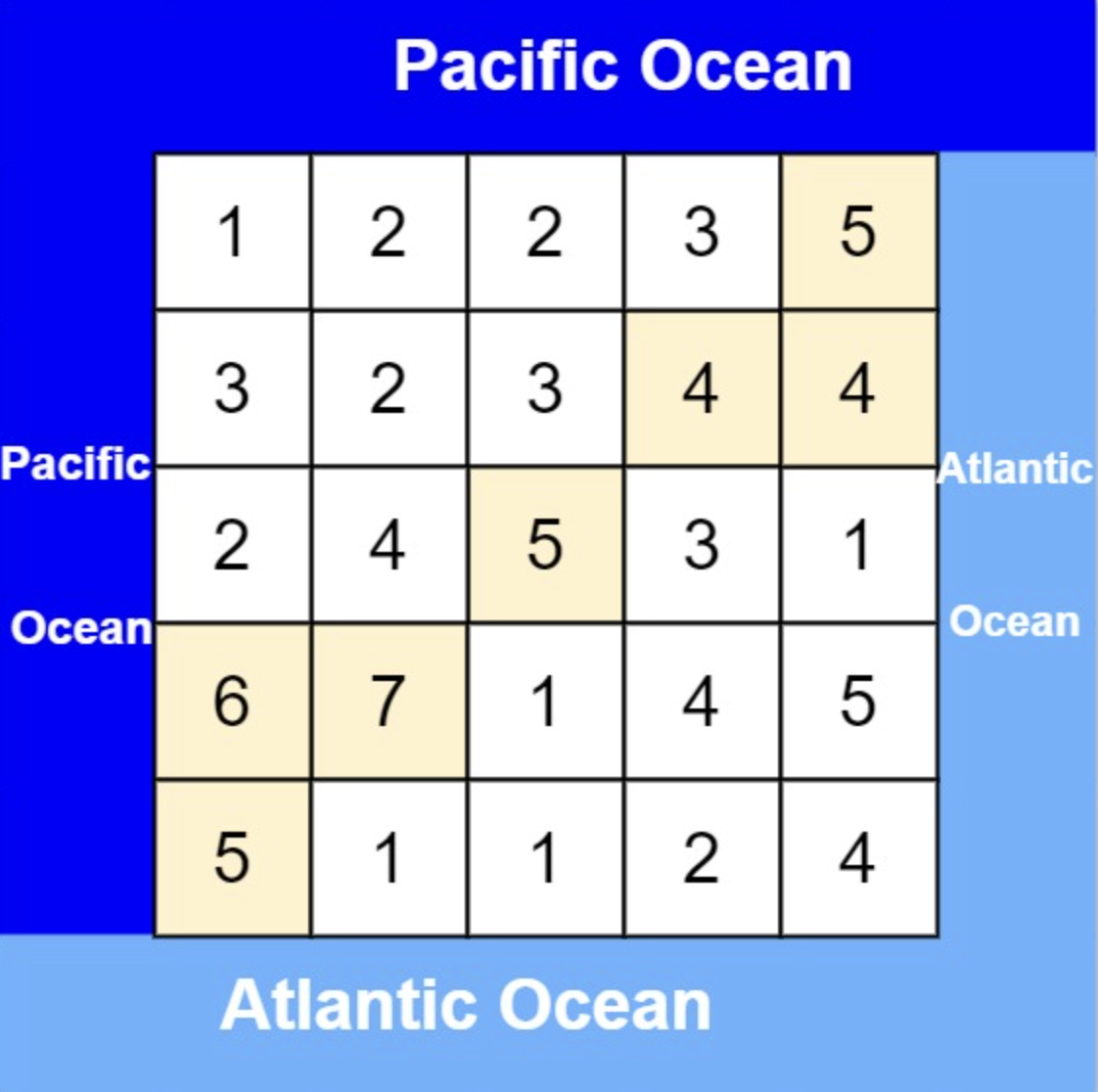
- 输入: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
- 输出: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
示例 2:
- 输入: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]]
- 输出: [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
提示:
- m == heights.length
- n == heights[r].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 200
- 0 <= heights[r][c] <= 10^5
思路
不少同学可能被这道题的题目描述迷惑了,其实就是找到哪些点 可以同时到达太平洋和大西洋。 流动的方式只能从高往低流。
那么一个比较直白的想法,其实就是 遍历每个点,然后看这个点 能不能同时到达太平洋和大西洋。
至于遍历方式,可以用dfs,也可以用bfs,以下用dfs来举例。
那么这种思路的实现代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1};
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
if (visited[x][y]) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= heights.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= heights[0].size()) continue;
if (heights[x][y] < heights[nextx][nexty]) continue; // 高度不合适
dfs (heights, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
return;
}
bool isResult(vector<vector<int>>& heights, int x, int y) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(heights.size(), vector<bool>(heights[0].size(), false));
// 深搜,将x,y出发 能到的节点都标记上。
dfs(heights, visited, x, y);
bool isPacific = false;
bool isAtlantic = false;
// 以下就是判断x,y出发,是否到达太平洋和大西洋
for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) {
if (visited[0][j]) {
isPacific = true;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i][0]) {
isPacific = true;
break;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) {
if (visited[heights.size() - 1][j]) {
isAtlantic = true;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i][heights[0].size() - 1]) {
isAtlantic = true;
break;
}
}
if (isAtlantic && isPacific) return true;
return false;
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
// 遍历每一个点,看是否能同时到达太平洋和大西洋
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) {
if (isResult(heights, i, j)) result.push_back({i, j});
}
}
return result;
}
};
这种思路很直白,但很明显,以上代码超时了。 来看看时间复杂度。
遍历每一个节点,是 m * n,遍历每一个节点的时候,都要做深搜,深搜的时间复杂度是: m * n
那么整体时间复杂度 就是 O(m^2 * n^2) ,这是一个四次方的时间复杂度。
优化
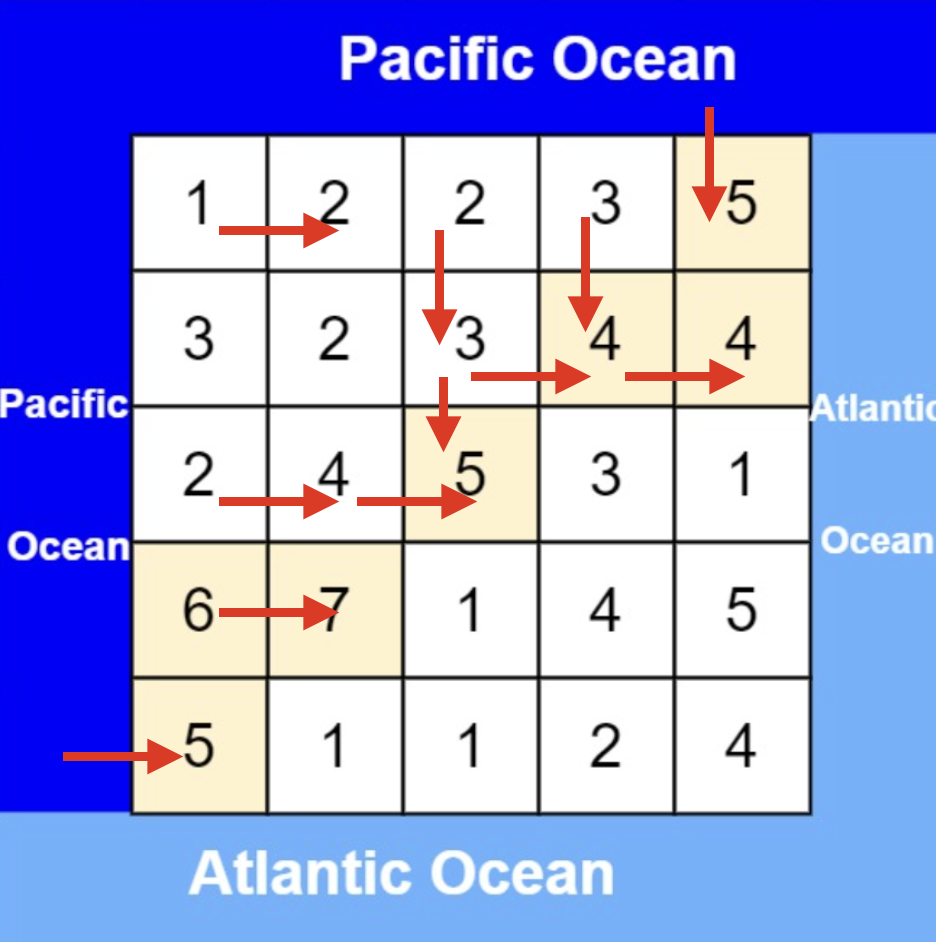
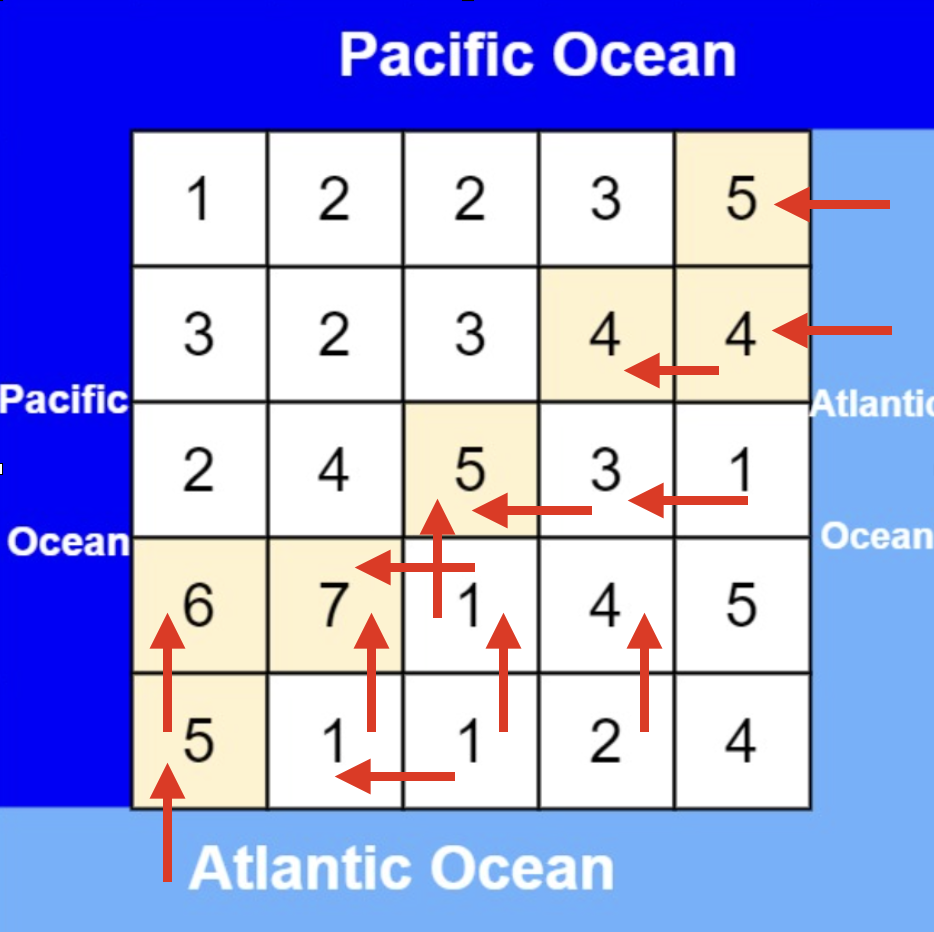
那么我们可以 反过来想,从太平洋边上的节点 逆流而上,将遍历过的节点都标记上。 从大西洋的边上节点 逆流而长,将遍历过的节点也标记上。 然后两方都标记过的节点就是既可以流太平洋也可以流大西洋的节点。
从太平洋边上节点出发,如图:
从大西洋边上节点出发,如图:
按照这样的逻辑,就可以写出如下遍历代码:(详细注释)
(如果对dfs基础内容就不懂,建议看 「代码随想录」DFS算法精讲!,还可以顺便解决 797. 所有可能的路径)
class Solution {
private:
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; // 保存四个方向
// 从低向高遍历,注意这里visited是引用,即可以改变传入的pacific和atlantic的值
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
if (visited[x][y]) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 向四个方向遍历
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
// 超过边界
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= heights.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= heights[0].size()) continue;
// 高度不合适,注意这里是从低向高判断
if (heights[x][y] > heights[nextx][nexty]) continue;
dfs (heights, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
return;
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
int n = heights.size();
int m = heights[0].size(); // 这里不用担心空指针,题目要求说了长宽都大于1
// 记录从太平洋边出发,可以遍历的节点
vector<vector<bool>> pacific = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
// 记录从大西洋出发,可以遍历的节点
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
// 从最上最下行的节点出发,向高处遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs (heights, pacific, i, 0); // 遍历最左列,接触太平洋
dfs (heights, atlantic, i, m - 1); // 遍历最右列,接触大西
}
// 从最左最右列的节点出发,向高处遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dfs (heights, pacific, 0, j); // 遍历最上行,接触太平洋
dfs (heights, atlantic, n - 1, j); // 遍历最下行,接触大西洋
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// 如果这个节点,从太平洋和大西洋出发都遍历过,就是结果
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) result.push_back({i, j});
}
}
return result;
}
};
时间复杂度分析, 关于dfs函数搜索的过程 时间复杂度是 O(n * m),这个大家比较容易想。
关键看主函数,那么每次dfs的时候,上面还是有for循环的。
第一个for循环,时间复杂度是:n * (n * m) 。
第二个for循环,时间复杂度是:m * (n * m)。
所以本题看起来 时间复杂度好像是 : n * (n * m) + m * (n * m) = (m * n) * (m + n) 。
其实这是一个误区,大家再自己看 dfs函数的实现,其实 有visited函数记录 走过的节点,而走过的节点是不会再走第二次的。
所以 调用dfs函数,只要参数传入的是 数组pacific,那么地图中 每一个节点其实就遍历一次,无论你调用多少次。
同理,调用 dfs函数,只要 参数传入的是 数组atlantic,地图中每个节点也只会遍历一次。
所以,以下这段代码的时间复杂度是 2 * n * m。 地图用每个节点就遍历了两次,参数传入pacific的时候遍历一次,参数传入atlantic的时候遍历一次。
// 从最上最下行的节点出发,向高处遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs (heights, pacific, i, 0); // 遍历最上行,接触太平洋
dfs (heights, atlantic, i, m - 1); // 遍历最下行,接触大西洋
}
// 从最左最右列的节点出发,向高处遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dfs (heights, pacific, 0, j); // 遍历最左列,接触太平洋
dfs (heights, atlantic, n - 1, j); // 遍历最右列,接触大西洋
}
那么本题整体的时间复杂度其实是: 2 * n * m + n * m ,所以最终时间复杂度为 O(n * m) 。
空间复杂度为:O(n * m) 这个就不难理解了。开了几个 n * m 的数组。
其他语言版本
Java
深度优先遍历:
class Solution {
// 四个位置
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
/**
* @param heights 题目给定的二维数组
* @param row 当前位置的行号
* @param col 当前位置的列号
* @param sign 记录是哪一条河,两条河中可以一个为 0,一个为 1
* @param visited 记录这个位置可以到哪条河
*/
public void dfs(int[][] heights, int row, int col, int sign, boolean[][][] visited) {
for (int[] current: position) {
int curRow = row + current[0], curCol = col + current[1];
// 越界
if (curRow < 0 || curRow >= heights.length || curCol < 0 || curCol >= heights[0].length)
continue;
// 高度不合适或者已经被访问过了
if (heights[curRow][curCol] < heights[row][col] || visited[curRow][curCol][sign]) continue;
visited[curRow][curCol][sign] = true;
dfs(heights, curRow, curCol, sign, visited);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int rowSize = heights.length, colSize = heights[0].length;
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
// 记录 [row, col] 位置是否可以到某条河,可以为 true,反之为 false;
// 假设太平洋的标记为 1,大西洋为 0
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize][2];
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = true;
visited[row][0][1] = true;
dfs(heights, row, colSize - 1, 0, visited);
dfs(heights, row, 0, 1, visited);
}
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = true;
visited[0][col][1] = true;
dfs(heights, rowSize - 1, col, 0, visited);
dfs(heights, 0, col, 1, visited);
}
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
// 如果该位置即可以到太平洋又可以到大西洋,就放入答案数组
if (visited[row][col][0] && visited[row][col][1])
ans.add(List.of(row, col));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
广度优先遍历:
class Solution {
// 四个位置
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
/**
* @param heights 题目给定的二维数组
* @param queue 记录可以到达边界的节点
* @param visited 记录这个位置可以到哪条河
*/
public void bfs(int[][] heights, Queue<int[]> queue, boolean[][][] visited) {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] curPos = queue.poll();
for (int[] current: position) {
int row = curPos[0] + current[0], col = curPos[1] + current[1], sign = curPos[2];
// 越界
if (row < 0 || row >= heights.length || col < 0 || col >= heights[0].length) continue;
// 高度不合适或者已经被访问过了
if (heights[row][col] < heights[curPos[0]][curPos[1]] || visited[row][col][sign]) continue;
visited[row][col][sign] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, col, sign});
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int rowSize = heights.length, colSize = heights[0].length;
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize][2];
// 队列,保存的数据为 [行号, 列号, 标记]
// 假设太平洋的标记为 1,大西洋为 0
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = true;
visited[row][0][1] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1, 0});
queue.add(new int[]{row, 0, 1});
}
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = true;
visited[0][col][1] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col, 0});
queue.add(new int[]{0, col, 1});
}
bfs(heights, queue, visited);
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
// 如果该位置即可以到太平洋又可以到大西洋,就放入答案数组
if (visited[row][col][0] && visited[row][col][1])
ans.add(List.of(row, col));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Python
深度优先遍历
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.position = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]] # 四个方向
# heights:题目给定的二维数组, row:当前位置的行号, col:当前位置的列号
# sign:记录是哪一条河,两条河中可以一个为 0,一个为 1
# visited:记录这个位置可以到哪条河
def dfs(self, heights: List[List[int]], row: int, col: int, sign: int, visited: List[List[List[int]]]):
for current in self.position:
curRow, curCol = row + current[0], col + current[1]
# 索引下标越界
if curRow < 0 or curRow >= len(heights) or curCol < 0 or curCol >= len(heights[0]): continue
# 不满足条件或者已经被访问过
if heights[curRow][curCol] < heights[row][col] or visited[curRow][curCol][sign]: continue
visited[curRow][curCol][sign] = True
self.dfs(heights, curRow, curCol, sign, visited)
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
rowSize, colSize = len(heights), len(heights[0])
# visited 记录 [row, col] 位置是否可以到某条河,可以为 true,反之为 false;
# 假设太平洋的标记为 1,大西洋为 0
# ans 用来保存满足条件的答案
ans, visited = [], [[[False for _ in range(2)] for _ in range(colSize)] for _ in range(rowSize)]
for row in range(rowSize):
visited[row][0][1] = True
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = True
self.dfs(heights, row, 0, 1, visited)
self.dfs(heights, row, colSize - 1, 0, visited)
for col in range(0, colSize):
visited[0][col][1] = True
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = True
self.dfs(heights, 0, col, 1, visited)
self.dfs(heights, rowSize - 1, col, 0, visited)
for row in range(rowSize):
for col in range(colSize):
# 如果该位置即可以到太平洋又可以到大西洋,就放入答案数组
if visited[row][col][0] and visited[row][col][1]:
ans.append([row, col])
return ans
广度优先遍历
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.position = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]]
# heights:题目给定的二维数组,visited:记录这个位置可以到哪条河
def bfs(self, heights: List[List[int]], queue: deque, visited: List[List[List[int]]]):
while queue:
curPos = queue.popleft()
for current in self.position:
row, col, sign = curPos[0] + current[0], curPos[1] + current[1], curPos[2]
# 越界
if row < 0 or row >= len(heights) or col < 0 or col >= len(heights[0]): continue
# 不满足条件或已经访问过
if heights[row][col] < heights[curPos[0]][curPos[1]] or visited[row][col][sign]: continue
visited[row][col][sign] = True
queue.append([row, col, sign])
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
rowSize, colSize = len(heights), len(heights[0])
# visited 记录 [row, col] 位置是否可以到某条河,可以为 true,反之为 false;
# 假设太平洋的标记为 1,大西洋为 0
# ans 用来保存满足条件的答案
ans, visited = [], [[[False for _ in range(2)] for _ in range(colSize)] for _ in range(rowSize)]
# 队列,保存的数据为 [行号, 列号, 标记]
# 假设太平洋的标记为 1,大西洋为 0
queue = deque()
for row in range(rowSize):
visited[row][0][1] = True
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = True
queue.append([row, 0, 1])
queue.append([row, colSize - 1, 0])
for col in range(0, colSize):
visited[0][col][1] = True
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = True
queue.append([0, col, 1])
queue.append([rowSize - 1, col, 0])
self.bfs(heights, queue, visited) # 广度优先遍历
for row in range(rowSize):
for col in range(colSize):
# 如果该位置即可以到太平洋又可以到大西洋,就放入答案数组
if visited[row][col][0] and visited[row][col][1]:
ans.append([row, col])
return ans
JavaScript
/**
* @description 深度搜索优先
* @param {number[][]} heights
* @return {number[][]}
*/
function pacificAtlantic(heights) {
const dir = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 1]];
const [rowSize, colSize] = [heights.length, heights[0].length];
const visited = Array.from({ length: rowSize }, _ =>
Array.from({ length: colSize }, _ => new Array(2).fill(false))
);
const result = [];
function dfs(heights, visited, x, y, sign) {
if (visited[x][y][sign]) {
return;
}
visited[x][y][sign] = true;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const nextX = x + dir[i][0];
const nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
continue;
}
if (heights[x][y] > heights[nextX][nextY]) {
continue;
}
dfs(heights, visited, nextX, nextY, sign);
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
dfs(heights, visited, i, 0, 0);
dfs(heights, visited, i, colSize - 1, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < colSize; i++) {
dfs(heights, visited, 0, i, 0);
dfs(heights, visited, rowSize - 1, i, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
if (visited[i][k][0] && visited[i][k][1]) {
result.push([i, k]);
}
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* @description 广度搜索优先
* @param {number[][]} heights
* @return {number[][]}
*/
function pacificAtlantic(heights) {
const dir = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 1]];
const [rowSize, colSize] = [heights.length, heights[0].length];
const visited = Array.from({ length: rowSize }, _ =>
Array.from({ length: colSize }, _ => new Array(2).fill(false))
);
const result = [];
function bfs(heights, visited, x, y, sign) {
if (visited[x][y][sign]) {
return;
}
visited[x][y][sign] = true;
const stack = [y, x];
while (stack.length !== 0) {
[x, y] = [stack.pop(), stack.pop()];
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const nextX = x + dir[i][0];
const nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
continue;
}
if (heights[x][y] > heights[nextX][nextY] || visited[nextX][nextY][sign]) {
continue;
}
visited[nextX][nextY][sign] = true;
stack.push(nextY, nextX);
}
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
bfs(heights, visited, i, 0, 0);
bfs(heights, visited, i, colSize - 1, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < colSize; i++) {
bfs(heights, visited, 0, i, 0);
bfs(heights, visited, rowSize - 1, i, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
if (visited[i][k][0] && visited[i][k][1]) {
result.push([i, k]);
}
}
}
return result;
}
go
dfs:
var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}
func pacificAtlantic(heights [][]int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
pacific := make([][]bool, len(heights))
atlantic := make([][]bool, len(heights))
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
pacific[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
atlantic[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
}
// 列
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0)
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, len(heights[0])-1)
}
// 行
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j)
dfs(heights, atlantic, len(heights)-1, j)
}
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res = append(res, []int{i, j})
}
}
}
return res
}
func dfs(heights [][]int, visited [][]bool, i, j int) {
visited[i][j] = true
for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
x, y := i+d[0], j+d[1]
if x < 0 || x >= len(heights) || y < 0 || y >= len(heights[0]) || heights[i][j] > heights[x][y] || visited[x][y] {
continue
}
dfs(heights, visited, x, y)
}
}
bfs:
var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}
func pacificAtlantic(heights [][]int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
pacific := make([][]bool, len(heights))
atlantic := make([][]bool, len(heights))
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
pacific[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
atlantic[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
}
// 列
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
bfs(heights, pacific, i, 0)
bfs(heights, atlantic, i, len(heights[0])-1)
}
// 行
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
bfs(heights, pacific, 0, j)
bfs(heights, atlantic, len(heights)-1, j)
}
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res = append(res, []int{i, j})
}
}
}
return res
}
func bfs(heights [][]int, visited [][]bool, i, j int) {
queue := make([][]int, 0)
queue = append(queue, []int{i, j})
visited[i][j] = true
for len(queue) > 0 {
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
x, y := cur[0]+d[0], cur[1]+d[1]
if x < 0 || x >= len(heights) || y < 0 || y >= len(heights[0]) || heights[cur[0]][cur[1]] > heights[x][y] || visited[x][y] {
continue
}
queue = append(queue, []int{x, y})
visited[x][y] = true
}
}
}
Rust
dfs:
impl Solution {
const DIRECTIONS: [(isize, isize); 4] = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)];
pub fn pacific_atlantic(heights: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let (m, n) = (heights.len(), heights[0].len());
let mut res = vec![];
let (mut pacific, mut atlantic) = (vec![vec![false; n]; m], vec![vec![false; n]; m]);
// 列
for i in 0..m {
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut pacific, i, 0);
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, i, n - 1);
}
for j in 0..n {
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut pacific, 0, j);
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, m - 1, j);
}
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res.push(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
}
}
}
res
}
pub fn dfs(heights: &[Vec<i32>], visited: &mut [Vec<bool>], i: usize, j: usize) {
visited[i][j] = true;
for (dx, dy) in Self::DIRECTIONS {
let (x, y) = (i as isize + dx, j as isize + dy);
if x < 0 || x >= heights.len() as isize || y < 0 || y >= heights[0].len() as isize {
continue;
}
let (x, y) = (x as usize, y as usize);
if !visited[x][y] && heights[x][y] >= heights[i][j] {
Self::dfs(heights, visited, x, y);
}
}
}
}
bfs:
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
const DIRECTIONS: [(isize, isize); 4] = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)];
pub fn pacific_atlantic(heights: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let (m, n) = (heights.len(), heights[0].len());
let mut res = vec![];
let (mut pacific, mut atlantic) = (vec![vec![false; n]; m], vec![vec![false; n]; m]);
// 列
for i in 0..m {
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut pacific, i, 0);
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, i, n - 1);
}
for j in 0..n {
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut pacific, 0, j);
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, m - 1, j);
}
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res.push(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
}
}
}
res
}
pub fn bfs(heights: &[Vec<i32>], visited: &mut [Vec<bool>], i: usize, j: usize) {
let mut queue = VecDeque::from([(i, j)]);
visited[i][j] = true;
while let Some((i, j)) = queue.pop_front() {
for (dx, dy) in Self::DIRECTIONS {
let (x, y) = (i as isize + dx, j as isize + dy);
if x < 0 || x >= heights.len() as isize || y < 0 || y >= heights[0].len() as isize {
continue;
}
let (x, y) = (x as usize, y as usize);
if !visited[x][y] && heights[x][y] >= heights[i][j] {
queue.push_back((x, y));
visited[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}