实现树:嵌套列表法
首先我们尝试用Python List来实现二叉树树数据结构;
递归的嵌套列表实现二叉树, 由具有3个元素的列表实现:
- 第1个元素为根节点的值;
- 第2个元素是左子树(所以也是一个列表);
- 第3个元素是右子树(所以也是一个列表)。

以右图的示例, 一个6节点的二叉树
根是myTree[0],左子树myTree[1],右子树myTree[2]
嵌套列表法的优点
子树的结构与树相同,是一种递归数据结构,很容易扩展到多叉树,仅需要增加列表元素即可

我们通过定义一系列函数来辅助操作嵌套列表
- BinaryTree创建仅有根节点的二叉树
- insertLeft/insertRight将新节点插入树中作为其直接的左/右子节点
- get/setRootVal则取得或返回根节点
- getLeft/RightChild返回左/右子树
嵌套列表法代码
def BinaryTree(r):
return [r, [], []]
def insertLeft(root, newBranch):
t = root.pop(1)
if len(t) > 1:
root.insert(1, [newBranch, t, []])
else:
root.insert(1, [newBranch, [], []])
return root
def insertRight(root, newBranch):
t = root.pop(2)
if len(t) > 1:
root.insert(2, [newBranch, [], t])
else:
root.insert(2, [newBranch, [], []])
return root
def getRootVal(root):
return root[0]
def setRootVal(root, newVal):
root[0] = newVal
def getLeftChild(root):
return root[1]
def getRightChild(root):
return root[2]
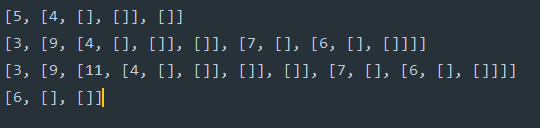
r = BinaryTree(3)
insertLeft(r, 4)
insertLeft(r, 5)
insertRight(r, 6)
insertRight(r, 7)
l = getLeftChild(r)
print(l)
setRootVal(l, 9)
print(r)
insertLeft(l, 11)
print(r)
print(getRightChild(getRightChild(r)))
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: