- registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary销毁回调
-
- requiresDestruction
-
- DisposableBeanAdapter的hasDestroyMethod销毁方法名
- DisposableBeanAdapter的hasApplicableProcessors
- DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry的registerDisposableBean
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary销毁回调
这里就数注册销毁回调方法,如果有的话。
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null);
if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) {
//有销毁接口的
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
//单例的情况,注册销毁回调
// Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction
// work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors,
// DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method.
registerDisposableBean(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
else {
//自定义的,注册到Scope
// A bean with a custom scope...
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope());
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'");
}
scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
}
}
requiresDestruction
检查是否是有销毁的方法注册的,有方法名都是可以的,或者有DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor处理器来判断的。
protected boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
return (bean.getClass() != NullBean.class &&
(DisposableBeanAdapter.hasDestroyMethod(bean, mbd) || (hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors() &&
DisposableBeanAdapter.hasApplicableProcessors(bean, getBeanPostProcessors()))));
}
DisposableBeanAdapter的hasDestroyMethod销毁方法名
实现DisposableBean和AutoCloseable 接口的,或者INFER_METHOD等于destroyMethodName 且有close,shutdown方法名的
public static boolean hasDestroyMethod(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
if (bean instanceof DisposableBean || bean instanceof AutoCloseable) {
return true;
}
String destroyMethodName = beanDefinition.getDestroyMethodName();
if (AbstractBeanDefinition.INFER_METHOD.equals(destroyMethodName)) {
return (ClassUtils.hasMethod(bean.getClass(), CLOSE_METHOD_NAME) ||
ClassUtils.hasMethod(bean.getClass(), SHUTDOWN_METHOD_NAME));
}
return StringUtils.hasLength(destroyMethodName);
}
DisposableBeanAdapter的hasApplicableProcessors
如果有处理器来处理的话。
public static boolean hasApplicableProcessors(Object bean, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(postProcessors)) {
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : postProcessors) {
if (processor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor dabpp = (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) processor;
if (dabpp.requiresDestruction(bean)) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry的registerDisposableBean
其实就是把bean注册进去,到时候回调就行。
public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
最后容器销毁的时候会调用:
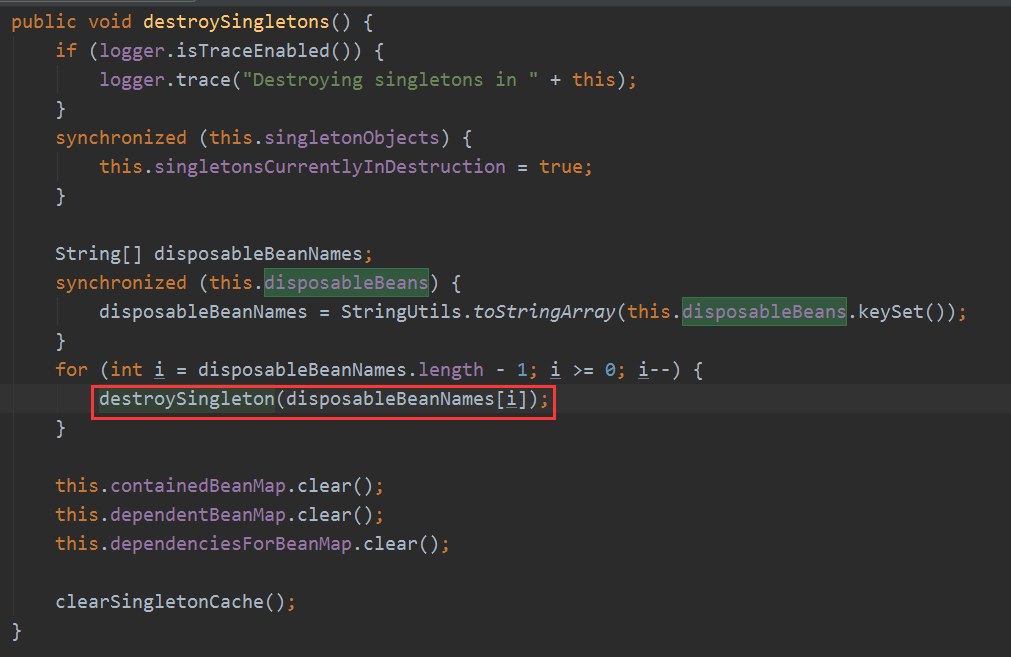
获取要销毁的bean:
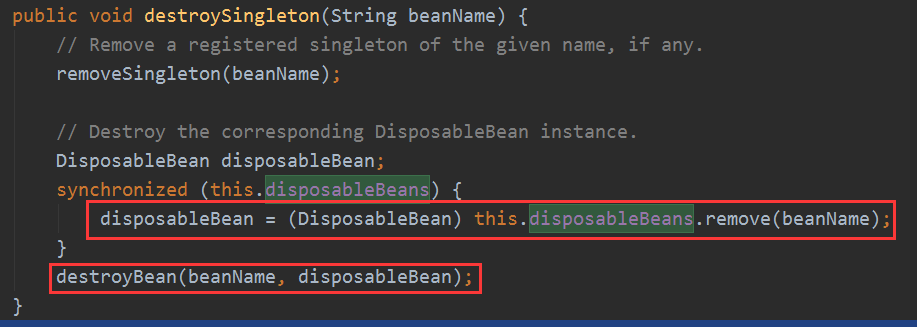
进行回调:
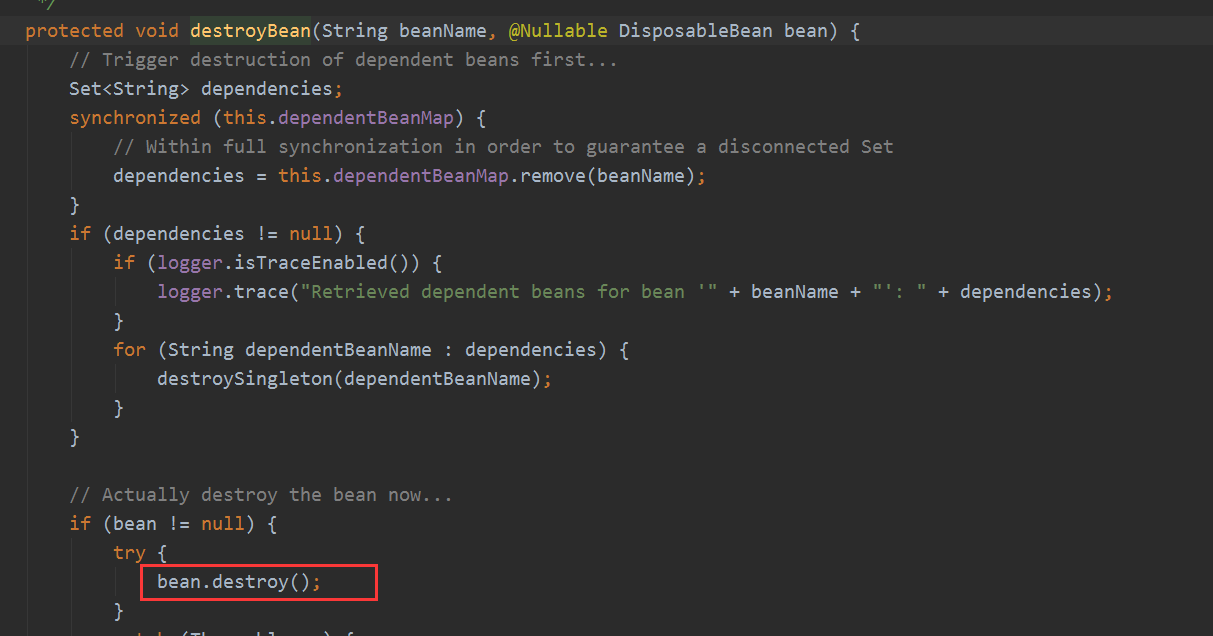
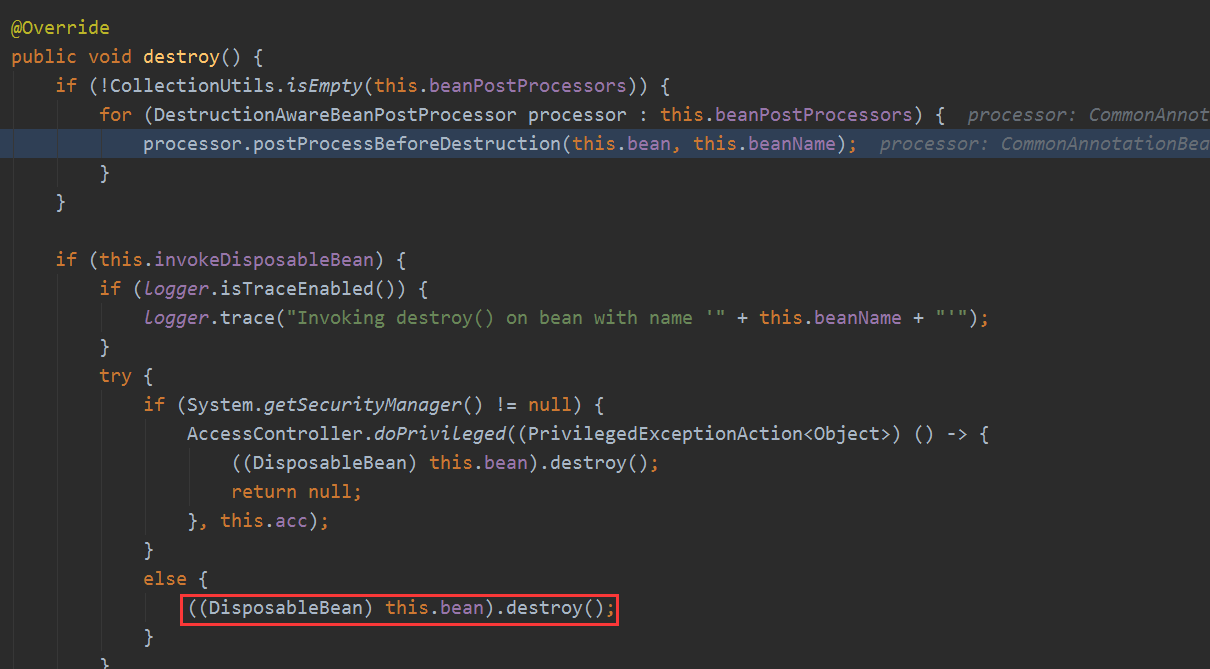
这样基本的getBean流程走完了,后面就讲一些细节的东西,比如循环依赖问题,后置处理器扩展问题等等。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。