1、Broker概述
Broker 在 RocketMQ 架构中的角色,就是存储消息,核心任务就是持久化消息,生产者发送消息给 Broker,消费者从 Broker 消费消息,其物理部署架构图如下:
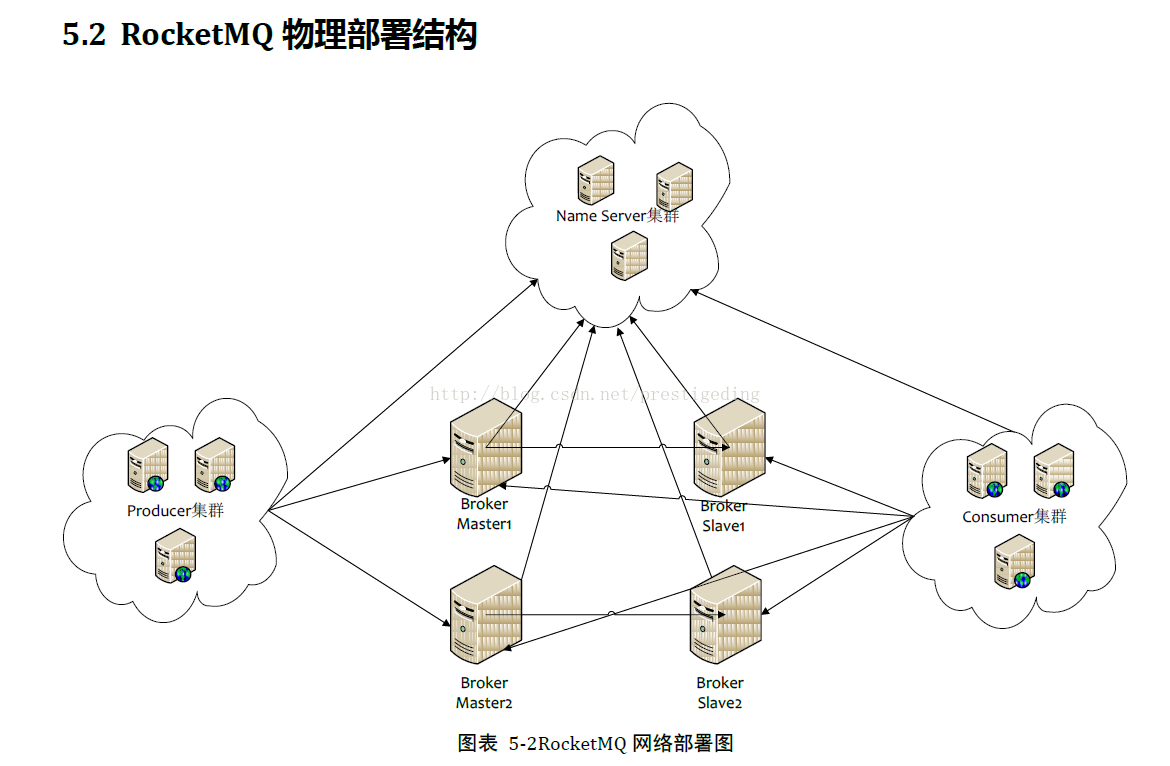


备注:以上摘录自官方 RocketMQ 设计文档。
上述基本描述了消息中间件的架构设计,不仅限于 RocketMQ,不同消息中间件的最大区别之一在消息的存储上。
2、Broker存储设计概要
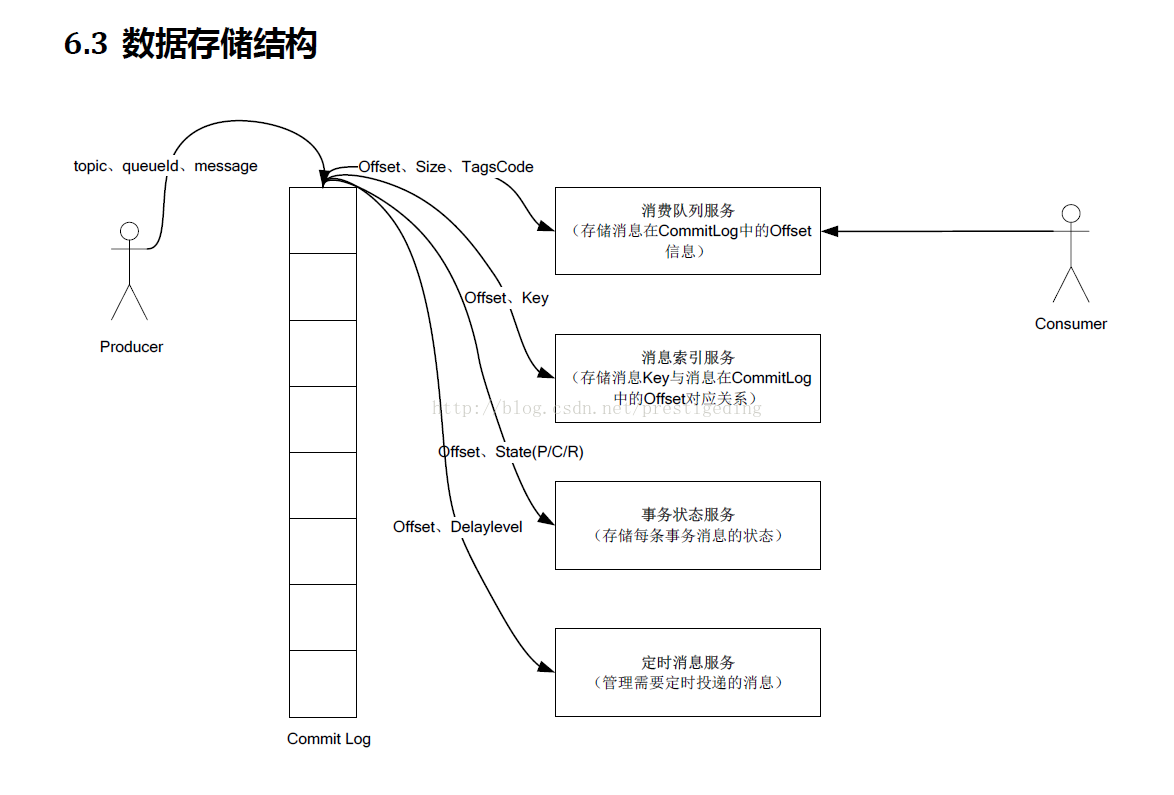
接下来从配置文件的角度来窥探 Broker 存储设计的关注点,对应代码(MessageStoreConfig)。
- storePathRootDir
设置Broker的存储根目录,默认为 $Broker_Home/store。 - storePathCommitLog
设置commitlog的存储目录,默认为$Broker_Home/store/commitlog。 - mapedFileSizeCommitLog
commitlog 文件的大小,默认为1G。 - mapedFileSizeConsumeQueue
consumeQueueSize,ConsumeQueue 存放的是定长的信息(20个字节,偏移量、size、tagscode),默认30w * ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE。 - enableConsumeQueueExt
是否开启 consumeQueueExt,默认为 false,就是如果消费端消息消费速度跟不上,是否创建一个扩展的 ConsumeQueue文件,如果不开启,应该会阻塞从 commitlog 文件中获取消息,并且 ConsumeQueue,应该是按topic独立的。 - mappedFileSizeConsumeQueueExt
扩展consume文件的大小,默认为48M。 - flushIntervalCommitLog
刷写 CommitLog 的间隔时间,RocketMQ 后台会启动一个线程,将消息刷写到磁盘,这个也就是该线程每次运行后等待的时间,默认为500毫秒。flush 操作,调用文件通道的force()方法。 - commitIntervalCommitLog
提交消息到 CommitLog 对应的文件通道的间隔时间,原理与上面类似;将消息写入到文件通道(调用FileChannel.write方法)得到最新的写指针,默认为200毫秒。 - useReentrantLockWhenPutMessage
在put message( 将消息按格式封装成msg放入相关队列时实用的锁机制:自旋或ReentrantLock)。 - flushIntervalConsumeQueue
刷写到ConsumeQueue的间隔,默认为1s。 - flushCommitLogLeastPages
每次 flush commitlog 时最小发生变化的页数。 - commitCommitLogLeastPages
每一次 commitlog 提交任务至少需要的页数。 - flushLeastPagesWhenWarmMapedFile
用字节0填充整个文件,每多少页刷盘一次,默认4096,异步刷盘模式生效。 - flushConsumeQueueLeastPages
一次刷盘至少需要的脏页数量,默认为2,针对 consuequeue 文件。 - putMsgIndexHightWater
当前版本未使用。
接下来从如下方面去深入其实现:
1)生产者发送消息
2)消息协议(格式)
3)消息存储、检索
4)消费队列维护
5)消息消费、重试等机制
2.1 消息发送
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.producer.DefaultMQProducerImpl sendDefaultImpl方法源码分析
rprivate SendResult sendDefaultImpl(//
Message msg, //
final CommunicationMode communicationMode, //
final SendCallback sendCallback, //
final long timeout//
) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
2.1.1 消息发送参数详解:
1、 Messagemsg;
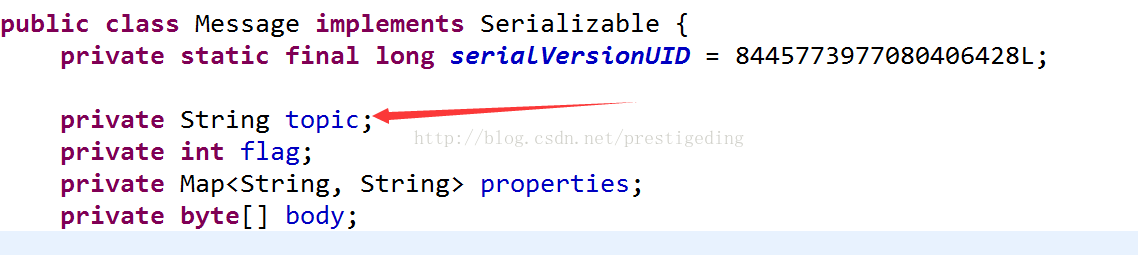
2、 communicationModecommunicationMode;
发送方式,SYNC(同步)、ASYNC(异步)、ONEWAY(单向,不关注返回)
3、 SendCallbacksendCallback;
异步消息发送回调函数。
4、 longtimeout;
消息发送超时时间。
2.2.2 消息发送流程
默认消息发送实现:
private SendResult sendDefaultImpl(//
Message msg, //
final CommunicationMode communicationMode, //
final SendCallback sendCallback, //
final long timeout//
) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
this.makeSureStateOK();
Validators.checkMessage(msg, this.defaultMQProducer);
final long invokeID = random.nextLong();
long beginTimestampFirst = System.currentTimeMillis();
long beginTimestampPrev = beginTimestampFirst;
long endTimestamp = beginTimestampFirst;
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic()); // @1
if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
MessageQueue mq = null;
Exception exception = null;
SendResult sendResult = null;
int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC ? 1 + this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1;
int times = 0;
String[] brokersSent = new String[timesTotal];
for (; times < timesTotal; times++) {
String lastBrokerName = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName();
MessageQueue tmpmq = this.selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName); // @2
if (tmpmq != null) {
mq = tmpmq;
brokersSent[times] = mq.getBrokerName();
try {
beginTimestampPrev = System.currentTimeMillis();
sendResult = this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout); // @3
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false);
switch (communicationMode) {
case ASYNC:
return null;
case ONEWAY:
return null;
case SYNC:
if (sendResult.getSendStatus() != SendStatus.SEND_OK) {
if (this.defaultMQProducer.isRetryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK()) {
continue;
}
}
return sendResult;
default:
break;
}
} catch (RemotingException e) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true); // @4
log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e);
log.warn(msg.toString());
exception = e;
continue;
} catch (MQClientException e) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true);
log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e);
log.warn(msg.toString());
exception = e;
continue;
} catch (MQBrokerException e) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true);
log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e);
log.warn(msg.toString());
exception = e;
switch (e.getResponseCode()) {
case ResponseCode.TOPIC_NOT_EXIST:
case ResponseCode.SERVICE_NOT_AVAILABLE:
case ResponseCode.SYSTEM_ERROR:
case ResponseCode.NO_PERMISSION:
case ResponseCode.NO_BUYER_ID:
case ResponseCode.NOT_IN_CURRENT_UNIT:
continue;
default:
if (sendResult != null) {
return sendResult;
}
throw e;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false);
log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, throw exception, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e);
log.warn(msg.toString());
log.warn("sendKernelImpl exception", e);
log.warn(msg.toString());
throw e;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
if (sendResult != null) {
return sendResult;
}
String info = String.format("Send [%d] times, still failed, cost [%d]ms, Topic: %s, BrokersSent: %s",
times,
System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTimestampFirst,
msg.getTopic(),
Arrays.toString(brokersSent));
info += FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.SEND_MSG_FAILED);
MQClientException mqClientException = new MQClientException(info, exception);
if (exception instanceof MQBrokerException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(((MQBrokerException) exception).getResponseCode());
} else if (exception instanceof RemotingConnectException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(ClientErrorCode.CONNECT_BROKER_EXCEPTION);
} else if (exception instanceof RemotingTimeoutException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(ClientErrorCode.ACCESS_BROKER_TIMEOUT);
} else if (exception instanceof MQClientException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(ClientErrorCode.BROKER_NOT_EXIST_EXCEPTION);
}
throw mqClientException;
}
List<String> nsList = this.getmQClientFactory().getMQClientAPIImpl().getNameServerAddressList();
if (null == nsList || nsList.isEmpty()) {
throw new MQClientException(
"No name server address, please set it." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.NAME_SERVER_ADDR_NOT_EXIST_URL), null).setResponseCode(ClientErrorCode.NO_NAME_SERVER_EXCEPTION);
}
throw new MQClientException("No route info of this topic, " + msg.getTopic() + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.NO_TOPIC_ROUTE_INFO),
null).setResponseCode(ClientErrorCode.NOT_FOUND_TOPIC_EXCEPTION);
主要的核心步骤如下:
代码@1:获取topic的路由信息。
代码@2:根据topic负载均衡算法选择一个MessageQueue。
代码@3:向 MessageQueue 发送消息。
代码@4:更新失败策略,主要用于规避发生故障的 broker,下文会详细介绍。
代码@5:如果是同步调用方式(SYNC),则执行失败重试策略,默认重试两次。
2、2.2.1 获取topic的路由信息
首先我们来思考一下,topic 的路由信息包含哪些内容。
消息的发布与订阅基于topic,路由发布信息以 topic 维度进行描述。
Broker 负载消息存储,一个 topic 可以分布在多台 Broker 上(负载均衡),每个 Broker 包含多个 Queue。队列元数据基于Broker来描述(QueueData:所在 BrokerName、读队列个数、写队列个数、权限、同步或异步)。
接下来从源码分析 tryToFindTopicPublishInfo方法,详细了解获取 Topic 的路由信息。
DefaultMQProducerImpl#tryToFindTopicPublishInfo
private TopicPublishInfo tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(final String topic) {
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic); // @1
if (null == topicPublishInfo || !topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
this.topicPublishInfoTable.putIfAbsent(topic, new TopicPublishInfo());
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic); // @2
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
}
if (topicPublishInfo.isHaveTopicRouterInfo() || topicPublishInfo.ok()) { //@3
return topicPublishInfo;
} else {
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, true, this.defaultMQProducer); //@4
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
return topicPublishInfo;
}
代码@1:从本地缓存(ConcurrentMap< String/* topic */, TopicPublishInfo>)中尝试获取,第一次肯定为空,走代码@2的流程。
代码@2:尝试从 NameServer 获取配置信息并更新本地缓存配置。
代码@3:如果找到可用的路由信息并返回。
代码@4:如果未找到路由信息,则再次尝试使用默认的 topic 去找路由配置信息。
接下来我们重点关注updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer方法。
MQClientInstance#updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer
public boolean updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(final String topic, boolean isDefault, DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer) {
try {
if (this.lockNamesrv.tryLock(LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { // @1
try {
TopicRouteData topicRouteData;
if (isDefault && defaultMQProducer != null) { //@2
topicRouteData = this.mQClientAPIImpl.getDefaultTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(defaultMQProducer.getCreateTopicKey(),
1000 * 3);
if (topicRouteData != null) {
for (QueueData data : topicRouteData.getQueueDatas()) {
int queueNums = Math.min(defaultMQProducer.getDefaultTopicQueueNums(), data.getReadQueueNums());
data.setReadQueueNums(queueNums);
data.setWriteQueueNums(queueNums);
}
}
} else {
topicRouteData = this.mQClientAPIImpl.getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, 1000 * 3); //@3
}
if (topicRouteData != null) {
TopicRouteData old = this.topicRouteTable.get(topic); //@4
boolean changed = topicRouteDataIsChange(old, topicRouteData); //@5
if (!changed) {
changed = this.isNeedUpdateTopicRouteInfo(topic); //@6
} else {
log.info("the topic[{}] route info changed, old[{}] ,new[{}]", topic, old, topicRouteData);
}
if (changed) { //@7
TopicRouteData cloneTopicRouteData = topicRouteData.cloneTopicRouteData();
for (BrokerData bd : topicRouteData.getBrokerDatas()) {
this.brokerAddrTable.put(bd.getBrokerName(), bd.getBrokerAddrs());
}
// Update Pub info //@8
{
TopicPublishInfo publishInfo = topicRouteData2TopicPublishInfo(topic, topicRouteData);
publishInfo.setHaveTopicRouterInfo(true);
Iterator<Entry<String, MQProducerInner>> it = this.producerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, MQProducerInner> entry = it.next();
MQProducerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
impl.updateTopicPublishInfo(topic, publishInfo);
}
}
}
// Update sub info //@9
{
Set<MessageQueue> subscribeInfo = topicRouteData2TopicSubscribeInfo(topic, topicRouteData);
Iterator<Entry<String, MQConsumerInner>> it = this.consumerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, MQConsumerInner> entry = it.next();
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
impl.updateTopicSubscribeInfo(topic, subscribeInfo);
}
}
}
log.info("topicRouteTable.put. Topic = {}, TopicRouteData[{}]", topic, cloneTopicRouteData);
this.topicRouteTable.put(topic, cloneTopicRouteData);
return true;
}
} else {
log.warn("updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer, getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer return null, Topic: {}", topic);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX) && !topic.equals(MixAll.DEFAULT_TOPIC)) {
log.warn("updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer Exception", e);
}
} finally {
this.lockNamesrv.unlock();
}
} else {
log.warn("updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer tryLock timeout {}ms", LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer Exception", e);
}
return false;
代码@1:为了避免重复从 NameServer 获取配置信息,在这里使用了ReentrantLock,并且设有超时时间。固定为3000s。
代码@2,@3的区别,一个是获取默认 topic 的配置信息,一个是获取指定 topic 的配置信息,该方法在这里就不跟踪进去了,具体的实现就是通过与 NameServer 的长连接 Channel 发送 GET_ROUTEINTO_BY_TOPIC (105)命令,获取配置信息。注意,次过程的超时时间为3s,由此可见,NameServer的实现要求高效。
代码@4、@5、@6:从这里开始,拿到最新的 topic 路由信息后,需要与本地缓存中的 topic 发布信息进行比较,如果有变化,则需要同步更新发送者、消费者关于该 topic 的缓存。
代码@7:更新发送者的缓存。
代码@8:更新订阅者的缓存(消费队列信息)。
至此tryToFindTopicPublishInfo 运行完毕,从 NameServe r获取 TopicPublishData,继续消息发送的第二个步骤,选取一个消息队列。
2、2.2.2 获取MessageQueue
核心源码:DefaultMQProducerImpl.sendDefaultImpl,对应 selectOneMessageQueue 方法。
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) {
if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) { // @1
try {
int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement(); //@2 start
for (int i = 0; i < tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); i++) {
int pos = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size();
if (pos < 0)
pos = 0;
MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(pos); //@2 end
if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName())) { //@3
if (null == lastBrokerName || mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName))
return mq;
}
}
final String notBestBroker = latencyFaultTolerance.pickOneAtLeast(); //@4
int writeQueueNums = tpInfo.getQueueIdByBroker(notBestBroker); //@5 start
if (writeQueueNums > 0) {
final MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
if (notBestBroker != null) {
mq.setBrokerName(notBestBroker);
mq.setQueueId(tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement() % writeQueueNums);
}
return mq;
} else {
latencyFaultTolerance.remove(notBestBroker); //@5 end
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error occurred when selecting message queue", e);
}
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
}
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName); //@6
代码@1: sendLatencyFaultEnable,是否开启消息失败延迟规避机制,该值在消息发送者那里可以设置,如果该值为false,直接从 topic 的所有队列中选择下一个,而不考虑该消息队列是否可用(比如Broker挂掉)。
代码@2-start–end,这里使用了本地线程变量 ThreadLocal 保存上一次发送的消息队列下标,消息发送使用轮询机制获取下一个发送消息队列。
代码@2对 topic 所有的消息队列进行一次验证,为什么要循环呢?因为加入了发送异常延迟,要确保选中的消息队列(MessageQueue)所在的Broker是正常的。
代码@3:判断当前的消息队列是否可用。
要理解代码@2,@3 处的逻辑,我们就需要理解 RocketMQ 发送消息延迟机制,具体实现类:MQFaultStrategy。
private long[] latencyMax = {50L, 100L, 550L, 1000L, 2000L, 3000L, 15000L};
private long[] notAvailableDuration = {0L, 0L, 30000L, 60000L, 120000L, 180000L, 600000L};
public void updateFaultItem(final String brokerName, final long currentLatency, boolean isolation) {
if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) {
long duration = computeNotAvailableDuration(isolation ? 30000 : currentLatency);
this.latencyFaultTolerance.updateFaultItem(brokerName, currentLatency, duration);
}
}
private long computeNotAvailableDuration(final long currentLatency) {
for (int i = latencyMax.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (currentLatency >= latencyMax[i])
return this.notAvailableDuration[i];
}
return 0;
latencyMax:最大延迟时间数值,在消息发送之前,先记录当前时间(start),然后消息发送成功或失败时记录当前时间(end),(end-start)代表一次消息延迟时间,发送错误时,updateFaultItem 中 isolation 为 true,与 latencyMax 中值进行比较时得值为 30s,也就时该 broke r在接下来得 600000L,也就时5分钟内不提供服务,等待该 Broker 的恢复。


计算出来的延迟值+加上本次消息的延迟值,设置 为FaultItem 的 startTimestamp,表示当前时间必须大于该 startTimestamp 时,该 broker 才重新参与 MessageQueue 的负载。
从@2–@3,一旦一个 MessageQueue 符合条件,即刻返回,但该 Topic 所在的所 有Broker全部标记不可用时,进入到下一步逻辑处理。(在此处,我们要知道,标记为不可用,并不代表真的不可用,Broker 是可以在故障期间被运营管理人员进行恢复的,比如重启)。
代码@4,5:根据 Broker 的 startTimestart 进行一个排序,值越小,排前面,然后再选择一个,返回(此时不能保证一定可用,会抛出异常,如果消息发送方式是同步调用,则有重试机制)。
接下来将进入到消息发送的第三步,发现消息。
2、2.2.3 根据MessageQueue向特定的Broker发送消息
消息发送方法为 sendKernelImpl。本文将不深入研究该方法,此刻理解为通过Product与Broker的长连接将消息发送给Broker,然后Broker将消息存储,并返回生产者。值得注意的是,如果消息发送模式为(SYNC)同步调用时,在生产者实现这边默认提供重试机制,通过(retryTimesWhenSendFailed)参数设置,默认为2,表示重试2次,也就时最多运行3次。
备注:异步消息发送的重试是在回调时。
本文主要分析了 RocketMQ 以同步方式发送消息的过程,异步模式与单向模式实现原理基本一样,异步只是增加了发送成功或失败的回掉方法。
思考题:
1、 消息发送时时异常处理思路;
1)NameServer 宕机
2)Broker 宕机
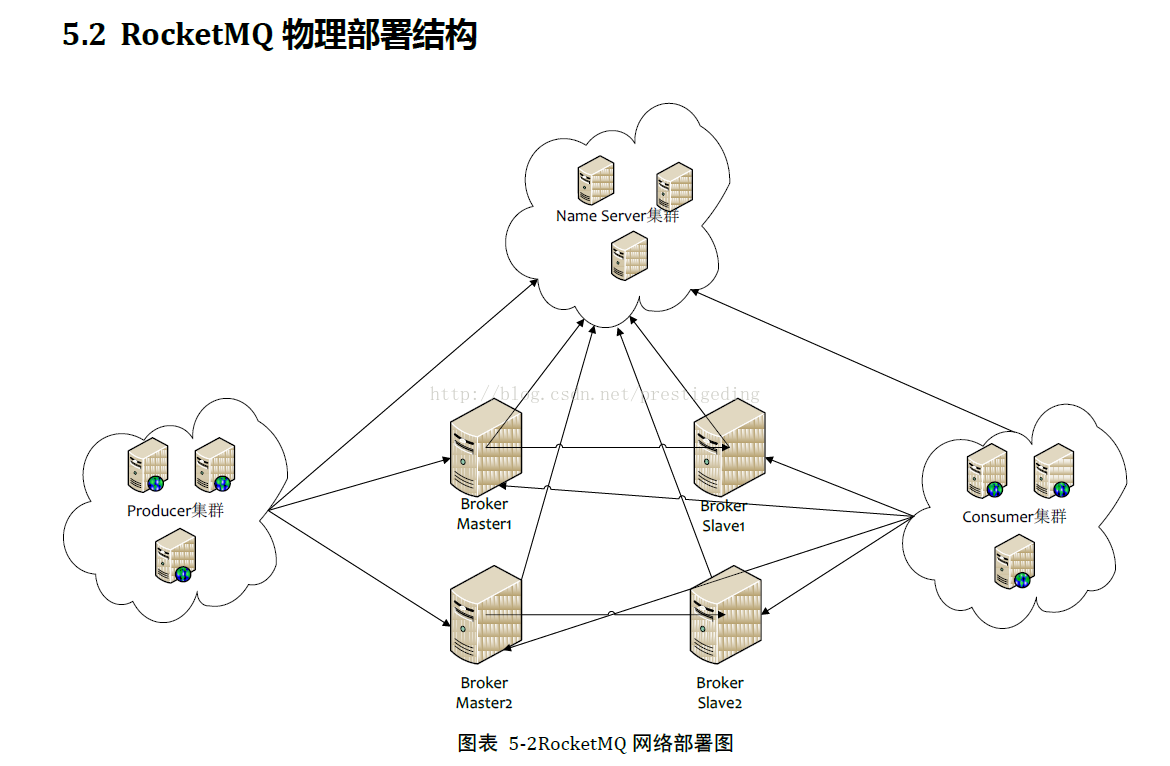
1、 消息发送者在同一时刻持有NameServer集群中的一个连接,用来及时获取broker等信息(topic路由信息),每一个Topic的队列分散在不同的Broker上,默认topic在Broker中对应4个发送队列,4个消息队列;
消息发送图解:

1、 NameServer挂机;
在发送消息阶段,如果生产者本地缓存中没有缓存 topic 的路由信息,则需要从 NameServer 获取,只有当所有 NameServer 都不可用时,此时会抛 MQClientException。如果所有的 NameServer 全部挂掉,并且生产者有缓存 Topic 的路由信息,此时依然可以发送消息。所以,NameServer 的宕机,通常不会对整个消息发送带来什么严重的问题。
2、 Broker挂机;
基础知识:消息生产者每隔 30s 从 NameServer 处获取最新的 Broker 存活信息(topic路由信息),Broker 每30s 向所有的 NameServer 报告自己的情况,故 Broker 的 down 机,Procuder 的最大可感知时间为 60s,在这 60s,消息发送会有什么影响呢?
此时分两种情况分别进行分析。
1)启用sendLatencyFaultEnable
由于使用了故障延迟机制,详细原理见上文详解,会对获取的 MQ 进行可用性验证,比如获取一个MessageQueue 发送失败,这时会对该 Broker 进行标记,标记该 Broker 在未来的某段时间内不会被选择到,默认为(5分钟,不可改变),所有此时只有当该 topic 全部的 broker 挂掉,才无法发送消息,符合高可用设计。
2)不启用sendLatencyFaultEnable = false
此时会出现消息发送失败的情况,因为默认情况下,procuder 每次发送消息,会采取轮询机制取下一个 MessageQueue,由于可能该 Message 所在的Broker挂掉,会抛出异常。因为一个 Broker 默认为一个 topic 分配4个 messageQueue,由于默认只重试2次,故消息有可能发送成功,有可能发送失败。
备注:本文是《RocketMQ技术内幕》的前期素材,建议关注笔者的书籍:《RocketMQ技术内幕》。