前言
简介图:
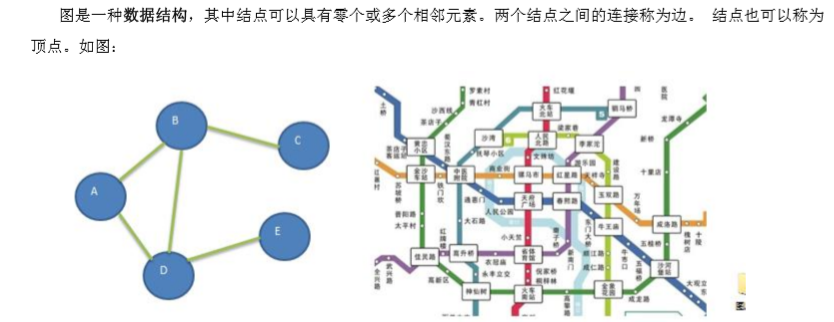
在数据的逻辑结构D=(KR)中,如果K中结点对于关系R的前趋和后继的个数不加限制,即仅含一种任意的关系,则称这种数据结构为图形结构。
来源百度百科
图形结构是一种比树形结构更复杂的非线性结构。在树形结构中,结点间具有分支层次关系,每一层上的结点只能和上一层中的至多一个结点相关,但可能和下一层的多个结点相关。而在图形结构中,任意两个结点之间都可能相关,即结点之间的邻接关系可以是任意的
然后就是盗图阶段:
后面就是一些基础常识,我找到一个比较全的:
https://www.cnblogs.com/songgj/p/9107797.html
正文
那么就来看一下图的深度遍历和广度遍历吧。
先来定义一个图:
public class Graph
{
private List<String> vertexList; //存储顶点集合
private int[,] edges; //存储图对应的邻结矩阵
private Boolean[] isVisited;// 判断是否访问了
int numOfEdges;
public Graph(int n){
vertexList = new List<string>();
edges = new int[8, 8];
isVisited = new Boolean[8];
}
/// <summary>
/// 增加节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="vertex">节点</param>
public void addVertex(string vertex)
{
vertexList.Add(vertex);
}
public void insertEdge(int x,int y,int weight)
{
//增加他们的连线 且设置他们的权重
edges[x, y] = 1;
edges[y, x] = 1;
numOfEdges++;
}
public void showEdges()
{
for (int i=0;i< isVisited.Length;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < isVisited.Length; j++)
{
Console.Write(edges[i,j]+" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
测试一下:
String[] Vertexs = { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8" };
//创建图对象
Graph graph = new Graph(Vertexs.Count());
//循环的添加顶点
foreach (String vertex in Vertexs)
{
graph.addVertex(vertex);
}
//更新边的关系
graph.insertEdge(0, 1, 1);
graph.insertEdge(0, 2, 1);
graph.insertEdge(1, 3, 1);
graph.insertEdge(1, 4, 1);
graph.insertEdge(3, 7, 1);
graph.insertEdge(4, 7, 1);
graph.insertEdge(2, 5, 1);
graph.insertEdge(2, 6, 1);
graph.insertEdge(5, 6, 1);
graph.showEdges();
Console.ReadKey();
结果:

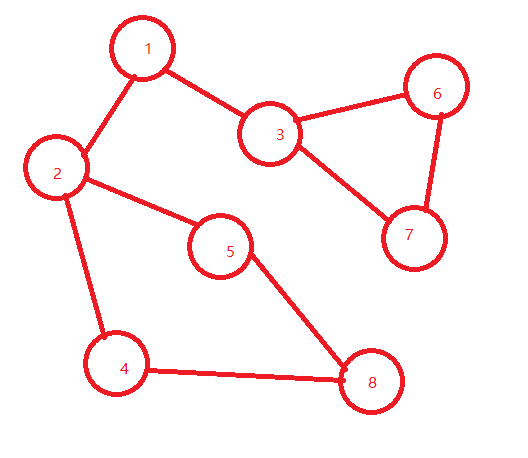
这么看可能不清晰哈,那么我画个图,看一下。
这是下面这张图哈:
深度遍历:
private int getFirstNeighbor(int index)
{
for (int j = 0; j < isVisited.Length; j++)
{
if (edges[index, j] > 0)
{
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 通过邻接节点来获取下一个节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="v1"></param>
/// <param name="v2"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int getNextNeighbor(int v1, int v2)
{
for (int j = v2+1; j < isVisited.Length; j++)
{
if (edges[v1, j] > 0)
{
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 深度遍历
/// </summary>
/// <param name="i"></param>
public void dfs(int i)
{
//打印遍历的值
Console.Write(vertexList[i]+" ");
isVisited[i] = true;
int w = getFirstNeighbor(i);
while (w != -1)
{
if (!isVisited[w])
{
dfs(w);
}
w = getNextNeighbor(i,w);
}
}
然后调用函数:
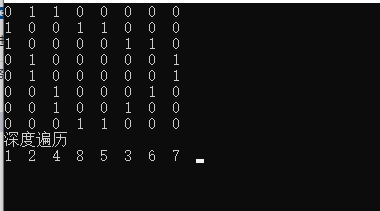
graph.dfs(0);
得到的结果是:
看下广度遍历吧:
//对一个结点进行广度优先遍历的方法
public void bfs(int i)
{
//打印遍历的值
Console.Write(vertexList[i] + " ");
LinkedList<int> queue = new LinkedList<int>();
queue.AddLast(i);
int u;
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
u = queue.First.Value;
queue.RemoveFirst();
int w = getFirstNeighbor(i);
while (w != -1)
{
if (!isVisited[w])
{
Console.Write(vertexList[w] + " ");
isVisited[w] = true;
queue.AddLast(w);
}
w = getNextNeighbor(u, w);
}
}
}
然后调用:
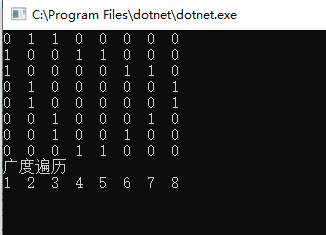
Console.WriteLine("广度遍历");
graph.bfs(0);
结果:
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: