使用过tomcat的都知道,我们的Host是会配置在Engine标签下面的在Server.xml中,所以这篇我们将要看的是另一个Container----------Host,下面是Host的继承关系图。
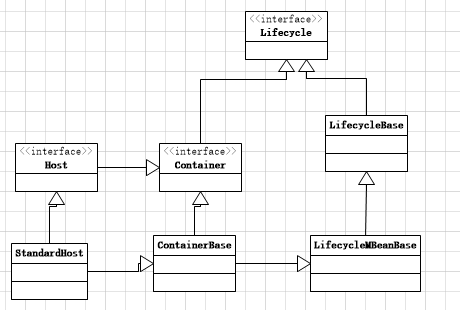
看Host源码可以看到,大部分都是get/set方法,之前分析我们知道,这个是跟Server.xml的元素属性相配合的,现在主要看set方法。
public interface Host extends Container {
// addAlias Event
public static final String ADD_ALIAS_EVENT = "addAlias";
// removeAlias Event
public static final String REMOVE_ALIAS_EVENT = "removeAlias";
// ------------------------------------------------------------- Properties
…….
//设置这个Host的root Xml,如果为空默认是${catalina.base}/conf/Enginename/Hostname/
public void setXmlBase(String xmlBase);
//返回这个Host的默认的配置文件
public File getConfigBaseFile();
//返回这个Host的application root
public String getAppBase();
//返回这个Host的application root file
public File getAppBaseFile();
//设置个Host 的application root
public void setAppBase(String appBase);
//设置是否自动发布
public void setAutoDeploy(boolean autoDeploy);
//设置Context Configuration Class
public void setConfigClass(String configClass);
//设置那个host的webapps是否自动发现和发布
public void setDeployOnStartup(boolean deployOnStartup);
//设置appBase的正则表达式,如果会自动发布,这个将被忽略
public void setDeployIgnore(String deployIgnore);
//启动和停止Context的Executor
public ExecutorService getStartStopExecutor();
//如果true,则会为Host创建appBase和xmlBase的目录
public void setCreateDirs(boolean createDirs);
//?
public void setUndeployOldVersions(boolean undeployOldVersions);
//Alias相关的方法
public void addAlias(String alias);
public String[] findAliases();
public void removeAlias(String alias);
跟之前一样我们从Catalina的createStartDigester开始来看init过后StandardHost的对象链以及Server.xml中关于Host的配置。看createStartDigester源码我们知道跟Host相关的ruleset是HostRuleSet。
digester.addRuleSet(new HostRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/"));
现在看HostRuleSet 类 addRuleInstances 方法:
public void addRuleInstances(Digester digester) {
//解析到…Engine\Host的时候创建对象,如果指定了className则使用className指定的类创建,如果没有则默认使用org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost digester.addObjectCreate(prefix + "Host",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost",
"className");
//设置Host标签属性给之前创建的Host对象
digester.addSetProperties(prefix + "Host");
// CopyParentClassLoaderRule 设置parent的classloader给child,这里的parent就是Engine,这里的child就是Host
digester.addRule(prefix + "Host",
new CopyParentClassLoaderRule());
// LifecycleListenerRule,看Host标签是否配置hostConfigClass属性,配置了就是使用创建LifecycleListener,如果没有设置,看parent也就是StandardEngine是否有这个属性,有则使用,最后都没有才会使用默认的org.apache.catalina.startup.HostConfig来创建,调用addLifecycleListener添加Listener
digester.addRule(prefix + "Host",
new LifecycleListenerRule
("org.apache.catalina.startup.HostConfig",
"hostConfigClass"));
//调用StandardEngine的addChild方法,传入StandardHost
digester.addSetNext(prefix + "Host",
"addChild",
"org.apache.catalina.Container");
//解析到Host/Alias标签,调用StandardHost的addAlias方法,参数是Alias标签的content
digester.addCallMethod(prefix + "Host/Alias",
"addAlias", 0);
//Cluster configuration start
//跟Engine一样,配置Cluster,不赘述,以后会详细分析Cluster
digester.addObjectCreate(prefix + "Host/Cluster",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties(prefix + "Host/Cluster");
digester.addSetNext(prefix + "Host/Cluster",
"setCluster",
"org.apache.catalina.Cluster");
//Cluster configuration end
//创建Host相关的Listener如果配置的话
digester.addObjectCreate(prefix + "Host/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties(prefix + "Host/Listener");
digester.addSetNext(prefix + "Host/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
//设置Realm,不赘述,后面会详细分析
digester.addRuleSet(new RealmRuleSet(prefix + "Host/"));
//设置Host的valve,这个会在处理请求的时候起作用,关于请求后面会详细分析
digester.addObjectCreate(prefix + "Host/Valve",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties(prefix + "Host/Valve");
digester.addSetNext(prefix + "Host/Valve",
"addValve",
"org.apache.catalina.Valve");
}
下面是Server.xml里面相对应的关于Host的配置
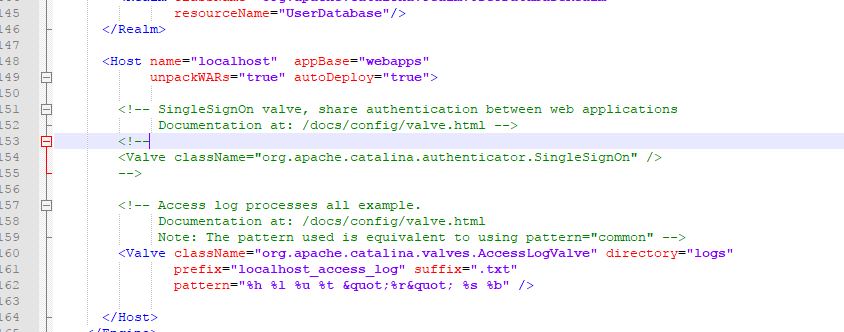
可以看出Host里面的几个属性,跟源码里面StandardHost的属性是匹配的,想熟悉配置,看源码是个最好的办法。
现在来看下StandardHost,看下它的构造函数
public StandardHost() {
super();
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardHostValve());
}
有相对应的StandardHostValve,这个会在处理请求的时候起作用,Container的组件都会有这个,tomcat的组件不涉及到请求的复杂部分还是很整齐划一的。
看源码可以发现几个跟使用tomcat的时候相熟悉的属性
private String appBase = "webapps";
private volatile File appBaseFile = null;
/**
* The XML root for this Host.
*/
private String xmlBase = null;
/**
* host's default config path
*/
private volatile File hostConfigBase = null;
/**
* The auto deploy flag for this Host.
*/
private boolean autoDeploy = true;
/**
* The Java class name of the default context configuration class
* for deployed web applications.
*/
//这是个重要的解析,负责解析Context
private String configClass =
"org.apache.catalina.startup.ContextConfig";
/**
* The Java class name of the default Context implementation class for
* deployed web applications.
*/
private String contextClass =
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext";
/**
* The deploy on startup flag for this Host.
*/
private boolean deployOnStartup = true;
/**
* deploy Context XML config files property.
*/
private boolean deployXML = !Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED;
/**
* Should XML files be copied to
* $CATALINA_BASE/conf/<engine>/<host> by default when
* a web application is deployed?
*/
private boolean copyXML = false;
/**
* The Java class name of the default error reporter implementation class
* for deployed web applications.
*/
private String errorReportValveClass =
"org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve";
/**
* Unpack WARs property.
*/
private boolean unpackWARs = true;
/**
* Work Directory base for applications.
*/
private String workDir = null;
/**
* Should we create directories upon startup for appBase and xmlBase
*/
private boolean createDirs = true;
因为ContainerBase上篇我们已经分析过了,现在看下StandardHost的XXXInternal方法,看源码发现只有StartInternal。
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
//给Host的pipleline添加一个Valve,默认是org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if(!found) {
Valve valve =
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass",
errorValve), t);
}
}
super.startInternal();
}
除了XXXInternal方法,我们还要关注几个跟配置有关的方法getAppBaseFile、getConfigBaseFile
public File getAppBaseFile() {
if (appBaseFile != null) {
return appBaseFile;
}
//appBase默认是webapps,我们也可以直接设置
File file = new File(getAppBase());
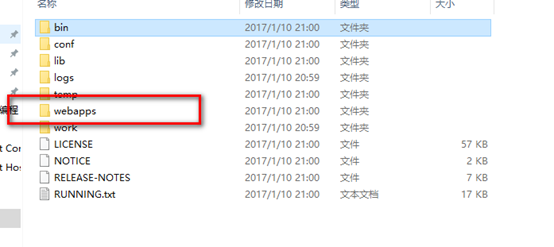
//如果不是绝对路径,我们就要将我们的和CatalinaBase(默认就是启动tomcat的时候进去的dir的parent dir)拼接,前面分析可知,这个路径就是bootstrap.jar所在的文件夹的路径,然后加上默认的webapps,可以看下图
if (!file.isAbsolute()) {
file = new File(getCatalinaBase(), file.getPath());
}
// Make it canonical if possible
try {
file = file.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// Ignore
}
this.appBaseFile = file;
return file;
}
public File getConfigBaseFile() {
if (hostConfigBase != null) {
return hostConfigBase;
}
String path = null;
if (getXmlBase()!=null) {
path = getXmlBase();
} else {
//开始拼接Confg
StringBuilder xmlDir = new StringBuilder("conf");
Container parent = getParent();
if (parent instanceof Engine) {
//Config/Engine的名字
xmlDir.append('/');
xmlDir.append(parent.getName());
}
xmlDir.append('/');
//Config/这个Houst所在的Engine的名字/这个Host的名字
xmlDir.append(getName());
path = xmlDir.toString();
}
File file = new File(path);
if (!file.isAbsolute())
//不是绝对路径,就加上CatalinaBase
file = new File(getCatalinaBase(), path);
try {
file = file.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException e) {// ignore
}
this.hostConfigBase = file;
return file;
}
现在来看下上面Digester解析提到的HostConfig,它是个LifeCyecleListner,所以我们主要关注,lifecycleEvent 方法
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) {
try {
// StandardHost的配置设置到HostConfig
host = (Host) event.getLifecycle();
if (host instanceof StandardHost) {
setCopyXML(((StandardHost) host).isCopyXML());
setDeployXML(((StandardHost) host).isDeployXML());
setUnpackWARs(((StandardHost) host).isUnpackWARs());
//设置StandardContext类,创建Digester
setContextClass(((StandardHost) host).getContextClass());
}
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("hostConfig.cce", event.getLifecycle()), e);
return;
}
// PERIODIC_EVENT是backgroudProcess的时候触发
if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.PERIODIC_EVENT)) {
check();
} else if
//startInternal之前触发
(event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT)) {
beforeStart();
// start的时候触发
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.START_EVENT)) {
start();
//stop的时候触发
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.STOP_EVENT)) {
stop();
}
}
基于HostConfig的重要和复杂性,我们下篇单独来分析。
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: