前言
在之前使用Nacos持久化规则的文档中,最后发现只能使用Nacos推送配置到控制台,那么怎么实现控制台和Nacos的双向同步呢?
这里不直接提供解决方案,我们还是先分析下控制台的源码。
下面我们分析下添加、查询流控规则的源码及流程。
核心类
首先分析下用到的相关类
RuleEntity
RuleEntity接口,其实现类就是这些规则对应的实体类了。
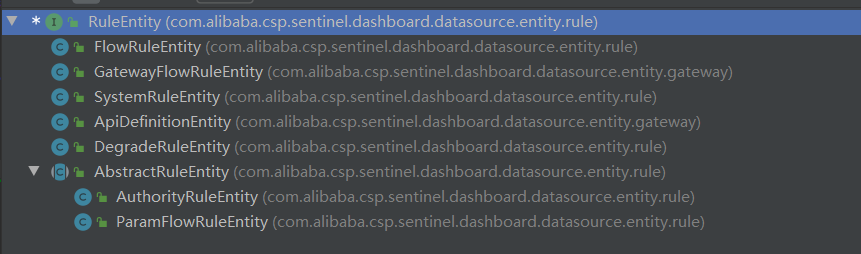
重点看下FlowRuleEntity源码:
public class FlowRuleEntity implements RuleEntity {
// 主键ID
private Long id;
// 后台应用名(客户端)
private String app;
// 后台应用IP
private String ip;
// 后台和控制台通信的端口 8719
private Integer port;
// 针对来源
private String limitApp;
// 资源名
private String resource;
/**
* 阈值类型
* 0为线程数;1为qps
*/
private Integer grade;
// 单机阈值
private Double count;
/**
* 流控模式
* 0为直接限流;1为关联限流;2为链路限流
*/
private Integer strategy;
// 关联限流时的关联资源
private String refResource;
/**
* 流控效果 快速失败 Warm Up 排队等待
* 0. default, 1. warm up, 2. rate limiter
*/
private Integer controlBehavior;
// warm up模式 预热时长
private Integer warmUpPeriodSec;
/**
* 速率限制器行为中的最大排队时间
*/
private Integer maxQueueingTimeMs;
// 是否集群
private boolean clusterMode;
/**
* 集群模式的流规则配置
*/
private ClusterFlowConfig clusterConfig;
// 创建时间
private Date gmtCreate;
// 修改时间
private Date gmtModified;
/**
* FlowRule=>FlowRuleEntity
*/
public static FlowRuleEntity fromFlowRule(String app, String ip, Integer port, FlowRule rule) {
// 省略.....
}
/**
* 实体类转为FlowRule
*/
@Override
public FlowRule toRule() {
// 省略.....
}
}
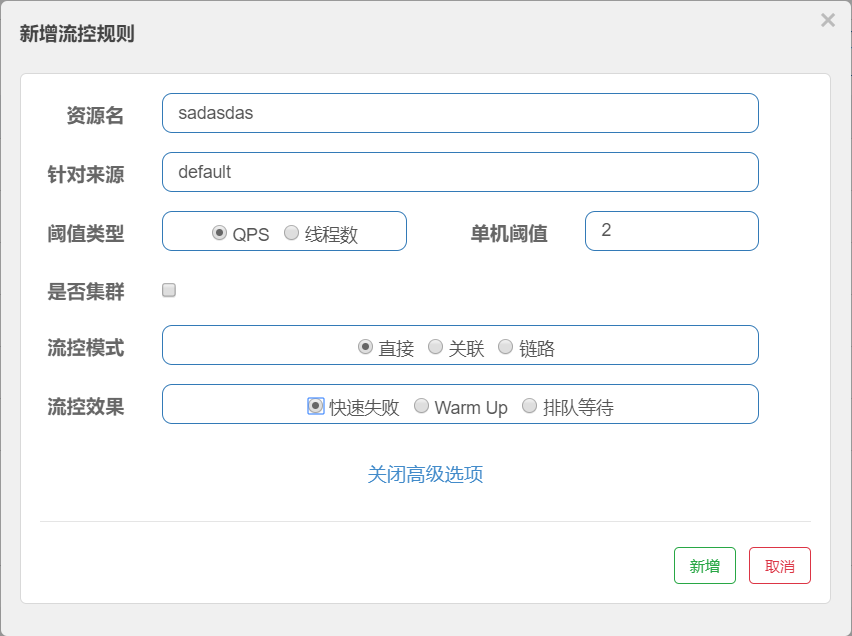
可以看到FlowRuleEntity就对应了界面中新增流控规则界面了。。
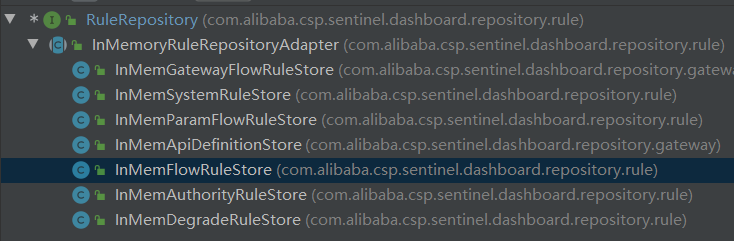
RuleRepository
RuleRepository是存储和查询规则的顶级接口,添加了增加、删除、查询规则的一系列方法。
public interface RuleRepository<T, ID> {
T save(T entity);
List<T> saveAll(List<T> rules);
T delete(ID id);
T findById(ID id);
List<T> findAllByMachine(MachineInfo machineInfo);
List<T> findAllByApp(String appName);
}
规则存储针对每种规则,都有对应的实现类,其抽象类InMemoryRuleRepositoryAdapter表示将规则存储在内存中,也是框架提供了唯一一个存储方式。
我们重点看下规则保存接口,这里会将所有规则保存到ConcurrentHashMap中。
@Override
public T save(T entity) {
// 1. 设置ID
if (entity.getId() == null) {
entity.setId(nextId());
}
// 2. 调用子类处理实体类
T processedEntity = preProcess(entity);
if (processedEntity != null) {
// 3. 将规则添加到ConcurrentHashMap,ID为KEY,规则为Value
allRules.put(processedEntity.getId(), processedEntity);
// 4. 将规则添加到ConcurrentHashMap,MachineInfo为KEY,所有的规则为Value
machineRules.computeIfAbsent(MachineInfo.of(processedEntity.getApp(), processedEntity.getIp(),
processedEntity.getPort()), e -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>(32))
.put(processedEntity.getId(), processedEntity);
// 5. 将规则添加到ConcurrentHashMap,后台应用名为KEY,所有的规则为Value
appRules.computeIfAbsent(processedEntity.getApp(), v -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>(32))
.put(processedEntity.getId(), processedEntity);
}
return processedEntity;
}
SentinelApiClient
SentinelApiClient类主要负责与 Sentinel 客户端通信,会发送HTTP调用客户端的API接口进行数据交互。
定义了很多常量,大部分都是API路径。
private static final String RESOURCE_URL_PATH = "jsonTree";
private static final String CLUSTER_NODE_PATH = "clusterNode";
private static final String GET_RULES_PATH = "getRules";
private static final String SET_RULES_PATH = "setRules";
private static final String GET_PARAM_RULE_PATH = "getParamFlowRules";
private static final String SET_PARAM_RULE_PATH = "setParamFlowRules";
private static final String FETCH_CLUSTER_MODE_PATH = "getClusterMode";
private static final String MODIFY_CLUSTER_MODE_PATH = "setClusterMode";
private static final String FETCH_CLUSTER_CLIENT_CONFIG_PATH = "cluster/client/fetchConfig";
private static final String MODIFY_CLUSTER_CLIENT_CONFIG_PATH = "cluster/client/modifyConfig";
private static final String FETCH_CLUSTER_SERVER_BASIC_INFO_PATH = "cluster/server/info";
private static final String MODIFY_CLUSTER_SERVER_TRANSPORT_CONFIG_PATH = "cluster/server/modifyTransportConfig";
private static final String MODIFY_CLUSTER_SERVER_FLOW_CONFIG_PATH = "cluster/server/modifyFlowConfig";
private static final String MODIFY_CLUSTER_SERVER_NAMESPACE_SET_PATH = "cluster/server/modifyNamespaceSet";
private static final String FETCH_GATEWAY_API_PATH = "gateway/getApiDefinitions";
private static final String MODIFY_GATEWAY_API_PATH = "gateway/updateApiDefinitions";
private static final String FETCH_GATEWAY_FLOW_RULE_PATH = "gateway/getRules";
private static final String MODIFY_GATEWAY_FLOW_RULE_PATH = "gateway/updateRules";
private static final String FLOW_RULE_TYPE = "flow";
private static final String DEGRADE_RULE_TYPE = "degrade";
private static final String SYSTEM_RULE_TYPE = "system";
private static final String AUTHORITY_TYPE = "authority";
接下来看下SentinelApiClient中的setRulesAsync方法,它的作用主要是异步请求客户端设置规则。
/**
* 异步请求客户端设置规则
* @param app 应用名
* @param ip 应用IP
* @param port 通信端口
* @param type 规则类型
* @param entities 规则
* @return
*/
private CompletableFuture<Void> setRulesAsync(String app, String ip, int port, String type, List<? extends RuleEntity> entities) {
try {
// 1. 检查参数
AssertUtil.notNull(entities, "rules cannot be null");
AssertUtil.notEmpty(app, "Bad app name");
AssertUtil.notEmpty(ip, "Bad machine IP");
AssertUtil.isTrue(port > 0, "Bad machine port");
// 2. 规则集合转为Json
String data = JSON.toJSONString(
entities.stream().map(r -> r.toRule()).collect(Collectors.toList()));
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>(2);
// 3. 设置请求参数
params.put("type", type);
params.put("data", data);
// 4. 发送请求
return executeCommand(app, ip, port, SET_RULES_PATH, params, true)
.thenCompose(r -> {
if ("success".equalsIgnoreCase(r.trim())) {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(null);
}
return AsyncUtils.newFailedFuture(new CommandFailedException(r));
});
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("setRulesAsync API failed, type={}", type, e);
return AsyncUtils.newFailedFuture(e);
}
}
接下来看下SentinelApiClient中的executeCommand方法,它的作用就是执行请求了。
private CompletableFuture<String> executeCommand(String app, String ip, int port, String api, Map<String, String> params, boolean useHttpPost) {
// 1. 拼接请求URL http://192.168.1.20:8721/setRules
CompletableFuture<String> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
if (StringUtil.isBlank(ip) || StringUtil.isBlank(api)) {
future.completeExceptionally(new IllegalArgumentException("Bad URL or command name"));
return future;
}
StringBuilder urlBuilder = new StringBuilder();
urlBuilder.append("http://");
urlBuilder.append(ip).append(':').append(port).append('/').append(api);
if (params == null) {
params = Collections.emptyMap();
}
// 2. 执行GET请求,参数拼在URL后面
if (!useHttpPost || !isSupportPost(app, ip, port)) {
// Using GET in older versions, append parameters after url
if (!params.isEmpty()) {
if (urlBuilder.indexOf("?") == -1) {
urlBuilder.append('?');
} else {
urlBuilder.append('&');
}
urlBuilder.append(queryString(params));
}
return executeCommand(new HttpGet(urlBuilder.toString()));
} else {
// Using POST
// 3. 执行POST请求
return executeCommand(
postRequest(urlBuilder.toString(), params, isSupportEnhancedContentType(app, ip, port)));
}
}
最终请求会使用apache提供了httpClient执行请求,获取返回结果。
添加流控规则源码分析
1. 访问接口
首先在页面中添加一个流控规则,并F12打开开发者模式,对/app/get进行限流。
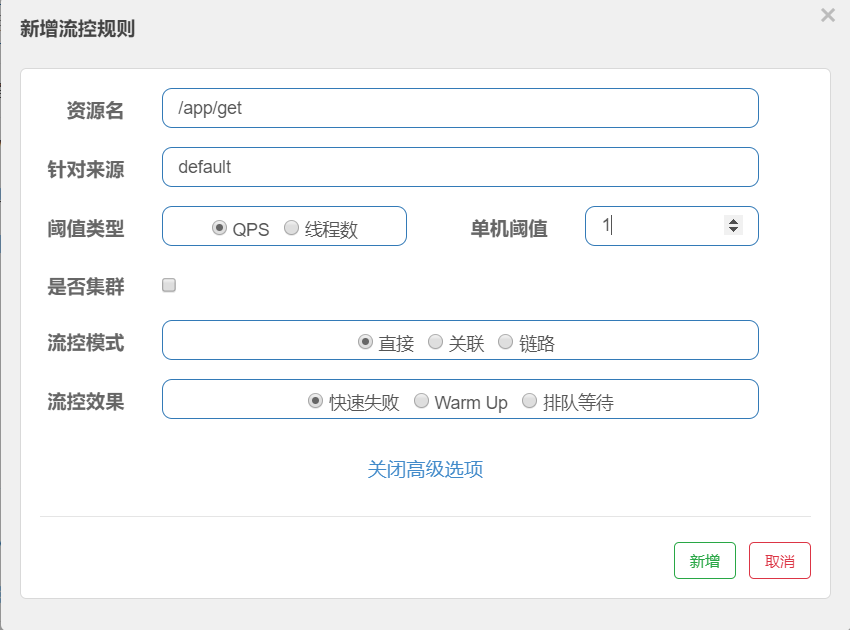
点击新增按钮,发送请求,我们看到是访问的/v1/flow/rule,然后注意下请求参数。
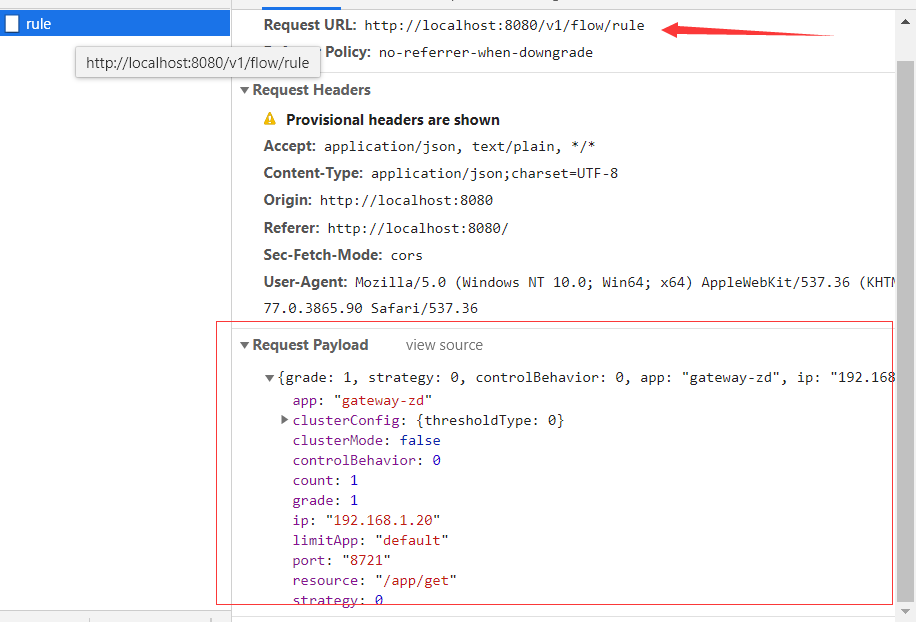
2. 控制台后台接口
上面的访问路径,对应的就是FlowControllerV1中的apiAddFlowRule控制器了,这是一个Spring MVC 接口。
这个接口主要是保存了规则在控制台的内存中,然后又调用了客户端的API,将规则发送给了客户端应用,具体怎么执行了,之前的核心类源码SentinelApiClient已经分析过了。
@PostMapping("/rule")
@AuthAction(PrivilegeType.WRITE_RULE)
public Result<FlowRuleEntity> apiAddFlowRule(@RequestBody FlowRuleEntity entity) {
// 1. 参数校验
Result<FlowRuleEntity> checkResult = checkEntityInternal(entity);
if (checkResult != null) {
return checkResult;
}
// 2. 设置附加参数
entity.setId(null);
Date date = new Date();
entity.setGmtCreate(date);
entity.setGmtModified(date);
entity.setLimitApp(entity.getLimitApp().trim());
entity.setResource(entity.getResource().trim());
try {
// 3. 保存流控规则,默认在内存,InMemoryRuleRepositoryAdapter
entity = repository.save(entity);
// http://192.168.1.20:8721/setRules
// 4. 调用客户端的API重新设置规则 SentinelApiClient
publishRules(entity.getApp(), entity.getIp(), entity.getPort()).get(5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return Result.ofSuccess(entity);
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable e = t instanceof ExecutionException ? t.getCause() : t;
logger.error("Failed to add new flow rule, app={}, ip={}", entity.getApp(), entity.getIp(), e);
return Result.ofFail(-1, e.getMessage());
}
}
3. 客户端后台接口
第二步中控制台调用了客户端的setRules接口,接下来我们看下客户端这个接口都做了什么。
setRules接口进入的是ModifyRulesCommandHandler处理器进行处理,其handle方法,主要是接受请求,然后根据不同的规则类型的管理器进行处理。
public CommandResponse<String> handle(CommandRequest request) {
// 1. XXX from 1.7.2, 当 fastjson 早于 1.2.12 时强制失败
if (VersionUtil.fromVersionString(JSON.VERSION) < FASTJSON_MINIMAL_VER) {
// fastjson版本太低
return CommandResponse.ofFailure(new RuntimeException("The \"fastjson-" + JSON.VERSION
+ "\" introduced in application is too old, you need fastjson-1.2.12 at least."));
}
// 2. 获取请求参数
String type = request.getParam("type");
String data = request.getParam("data");
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(data)) {
try {
data = URLDecoder.decode(data, "utf-8");
} catch (Exception e) {
RecordLog.info("Decode rule data error", e);
return CommandResponse.ofFailure(e, "decode rule data error");
}
}
RecordLog.info("Receiving rule change (type: {}): {}", type, data);
String result = "success";
// 3. 判断规则类型
if (FLOW_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
// 流控规则 解析参数为流控规则对象集合
List<FlowRule> flowRules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, FlowRule.class);
// 调用流量规则管理器加载规则 返回结果
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(flowRules);
if (!writeToDataSource(getFlowDataSource(), flowRules)) {
result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG;
}
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result);
} else if (AUTHORITY_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
List<AuthorityRule> rules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, AuthorityRule.class);
AuthorityRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
if (!writeToDataSource(getAuthorityDataSource(), rules)) {
result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG;
}
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result);
} else if (DEGRADE_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
List<DegradeRule> rules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, DegradeRule.class);
DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
if (!writeToDataSource(getDegradeDataSource(), rules)) {
result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG;
}
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result);
} else if (SYSTEM_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
List<SystemRule> rules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, SystemRule.class);
SystemRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
if (!writeToDataSource(getSystemSource(), rules)) {
result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG;
}
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result);
}
return CommandResponse.ofFailure(new IllegalArgumentException("invalid type"));
}
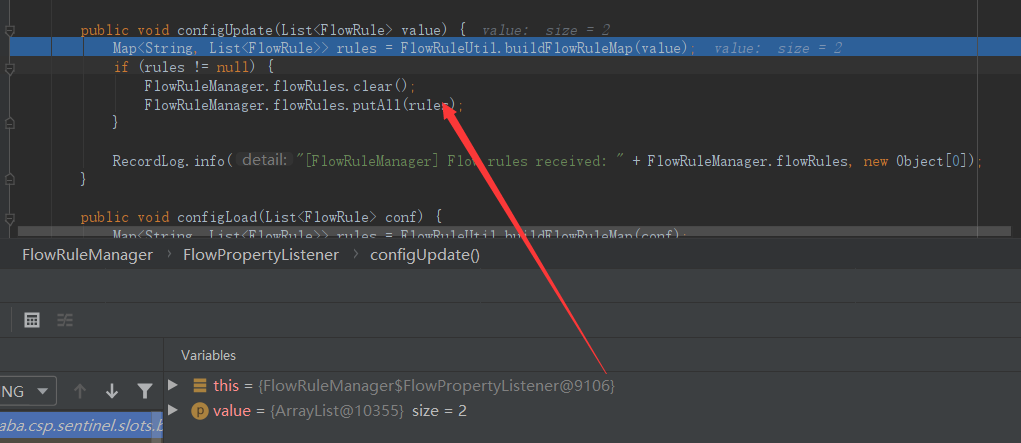
流控规则调用的是FlowRuleManager,其loadRules方法最终调用的就是DynamicSentinelProperty的updateValue方法。
可以看到DynamicSentinelProperty维护了之前流控规则,并接受了新的流控规则。
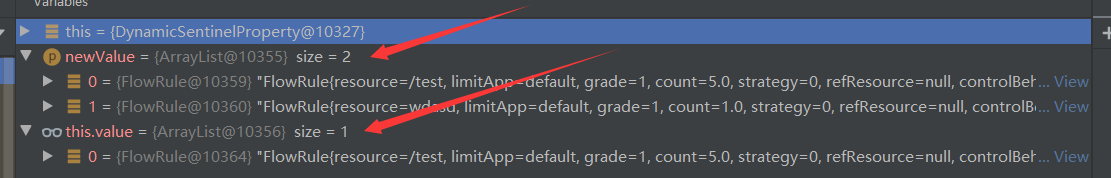
之后会调用管理器中的监听器并循环。
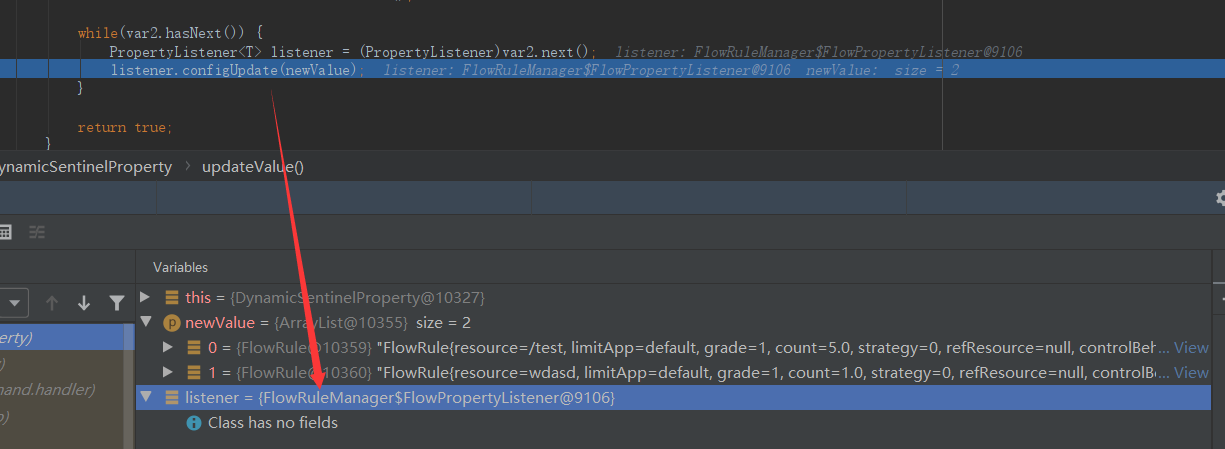
最终调用监听器的configUpdate方法,更新规则管理器中存放规则的ConcurrentHashMap,这样客户端的内存中流控规则也就更新了。
查询流控规则源码分析
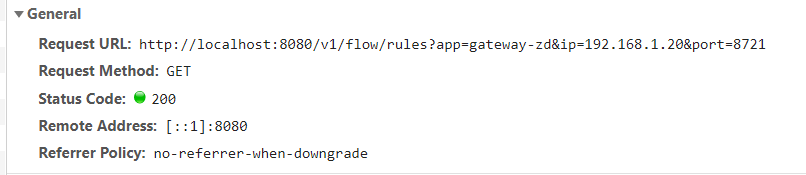
1. 访问接口
F12可以看到访问的是/v1/flow/rules接口。
/v1/flow/rules接口的逻辑处理如下:
@GetMapping("/rules")
@AuthAction(PrivilegeType.READ_RULE)
public Result<List<FlowRuleEntity>> apiQueryMachineRules(@RequestParam String app,
@RequestParam String ip,
@RequestParam Integer port) {
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(app)) {
return Result.ofFail(-1, "app can't be null or empty");
}
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(ip)) {
return Result.ofFail(-1, "ip can't be null or empty");
}
if (port == null) {
return Result.ofFail(-1, "port can't be null");
}
try {
// 1. 调用客户端API,查询规则 http://192.168.1.20:8721/getRules
List<FlowRuleEntity> rules = sentinelApiClient.fetchFlowRuleOfMachine(app, ip, port);
// 2. 将客户端查询到的规则 重新存放到控制台中,会事先清理控制台内存中的规则
rules = repository.saveAll(rules);
return Result.ofSuccess(rules);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
logger.error("Error when querying flow rules", throwable);
return Result.ofThrowable(-1, throwable);
}
}
2.客户端查询规则
控制台发出getRules请求后,是交给FetchActiveRuleCommandHandler处理器来进行处理。
@Override
public CommandResponse<String> handle(CommandRequest request) {
String type = request.getParam("type");
if ("flow".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
// 调用管理器获取规则
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(JSON.toJSONString(FlowRuleManager.getRules()));
} else if ("degrade".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(JSON.toJSONString(DegradeRuleManager.getRules()));
} else if ("authority".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(JSON.toJSONString(AuthorityRuleManager.getRules()));
} else if ("system".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(JSON.toJSONString(SystemRuleManager.getRules()));
} else {
return CommandResponse.ofFailure(new IllegalArgumentException("invalid type"));
}
}
在管理器中会将内存中的规则返回给控制台。
public static List<FlowRule> getRules() {
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<FlowRule>();
for (Map.Entry<String, List<FlowRule>> entry : flowRules.entrySet()) {
rules.addAll(entry.getValue());
}
return rules;
}
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: