1. RPC 调用流程分析
1.1 RPC基本介绍
(1)RPC(Remote Procedure Call)远程过程调用,是一个计算机通信协议。该协议允许运行于一台计算机的程序调用另一台计算机的子程序,而程序员无需额外地为这个交互作用编程。
(2)两个或多个应用程序都分布在不同的服务器上,它们之间的调用都像是本地方法调用一样。
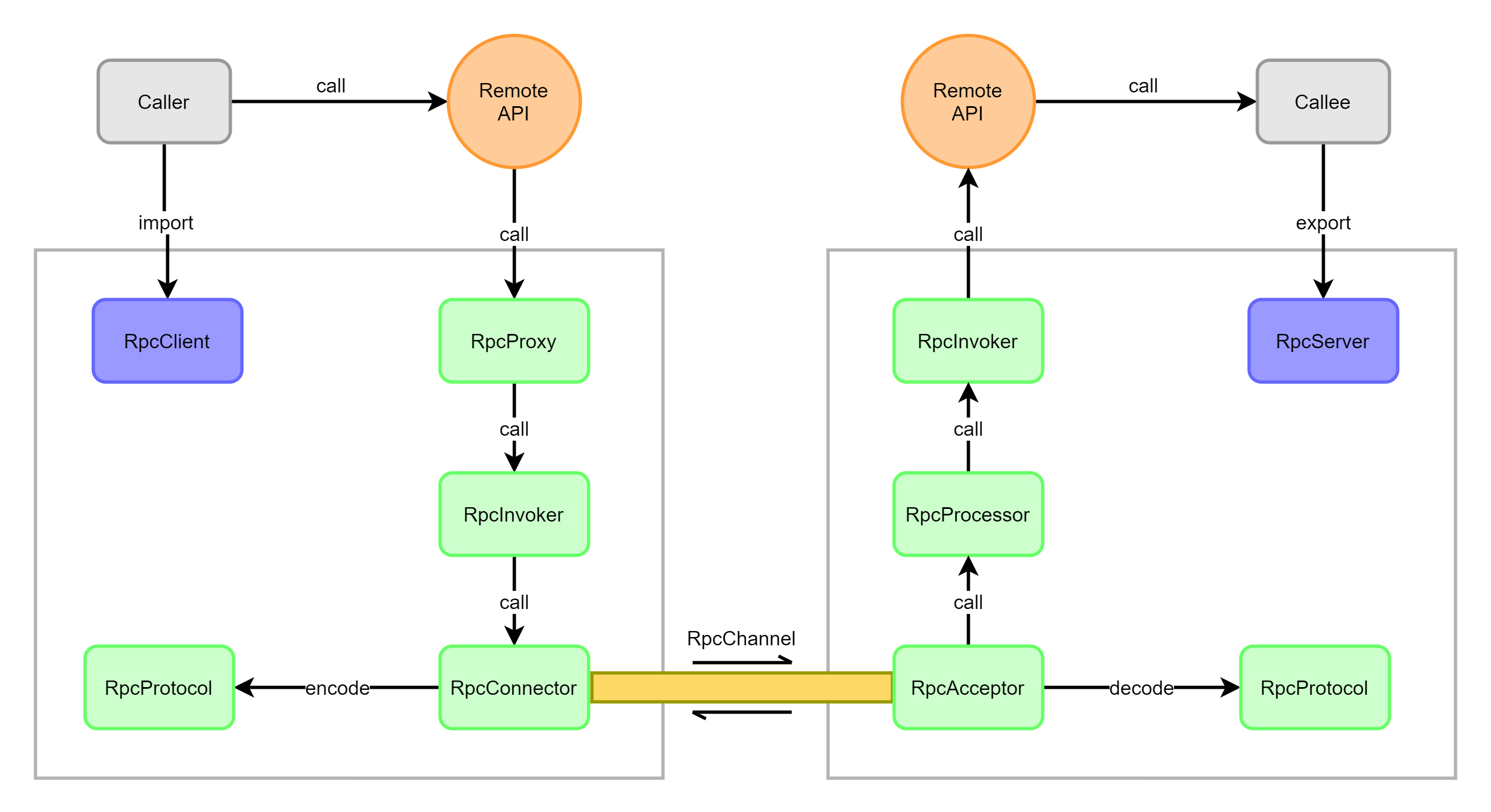
(3)常用的 RPC 框架有:比较知名的阿里的 Dubbo、google 的 gRPC、GO语言的 rpcx、Apache 的 thrift,Spring 旗下的 Spring Cloud。
1.2 RPC调用流程
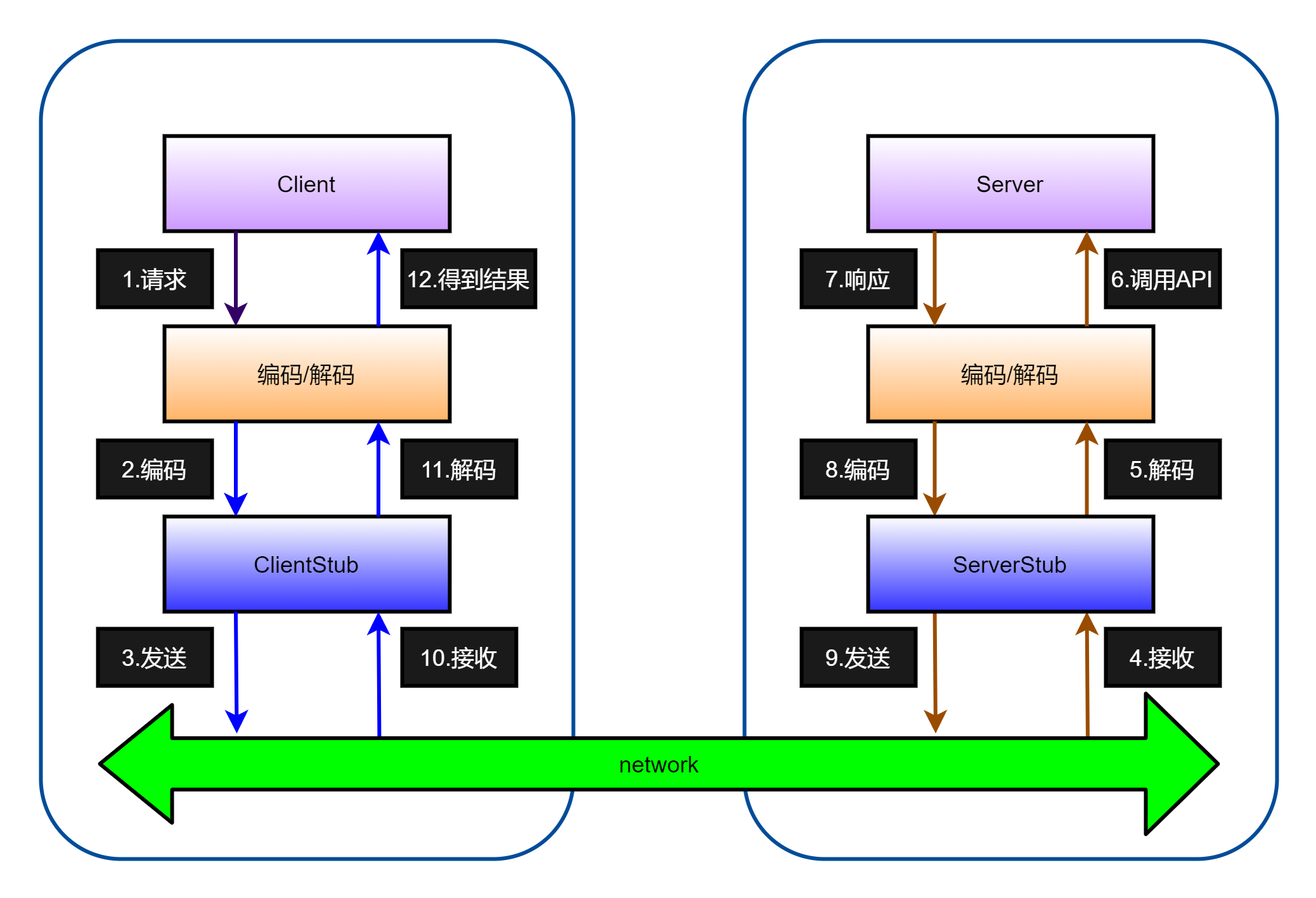
术语说明:在 RPC 中,Client 叫服务消费者,Server 叫服务提供者。
RPC调用流程说明:
(1)服务消费方(Client)以本地调用方式调用服务;
(2)client stub 接收到调用后负责将方法、参数等封装成能够进行网络传输的消息体;
(3)client stub 将消息进行编码并发送到服务端;
(4)server stub 收到消息后进行解码;
(5)server stub 根据解码结果调用本地的服务;
(6)本地服务执行并将结果返回给 server stub;
(7)server stub 将返回导入结果进行编码并发送至消费方;
(8)client stub 接收到消息并进行解码;
(9)服务消费方(client)得到结果。
小结:RPC 的目标就是将 2-8 这些步骤都封装起来,用户无需关心这些细节,可以像调用本地方法一样即可完成远程服务调用。
2.基于 Netty 实现 DubboRPC
2.1 需求说明
(1)Dubbo 底层使用了 Netty 作为网络通讯框架,要求用 Netty 实现一个简单的 RPC 框架。
(2)模仿 Dubbo,消费者和提供者约定接口和协议,消费者远程调用提供者的服务,提供者返回一个字符串,消费者打印提供者返回的数据。底层网络通信使用 Netty 4.1.20。
2.2 设计说明
(1)创建一个接口,定义抽象方法。用于消费者和提供者之间的约定。
(2)创建一个提供者,该类需要监听消费者的请求,并按照约定返回数据。
(3)创建一个消费者,该类需要透明的调用自己不存在的方法,内部需要使用 Netty 请求提供者返回数据。
(4)开发的分析图,如下所示。
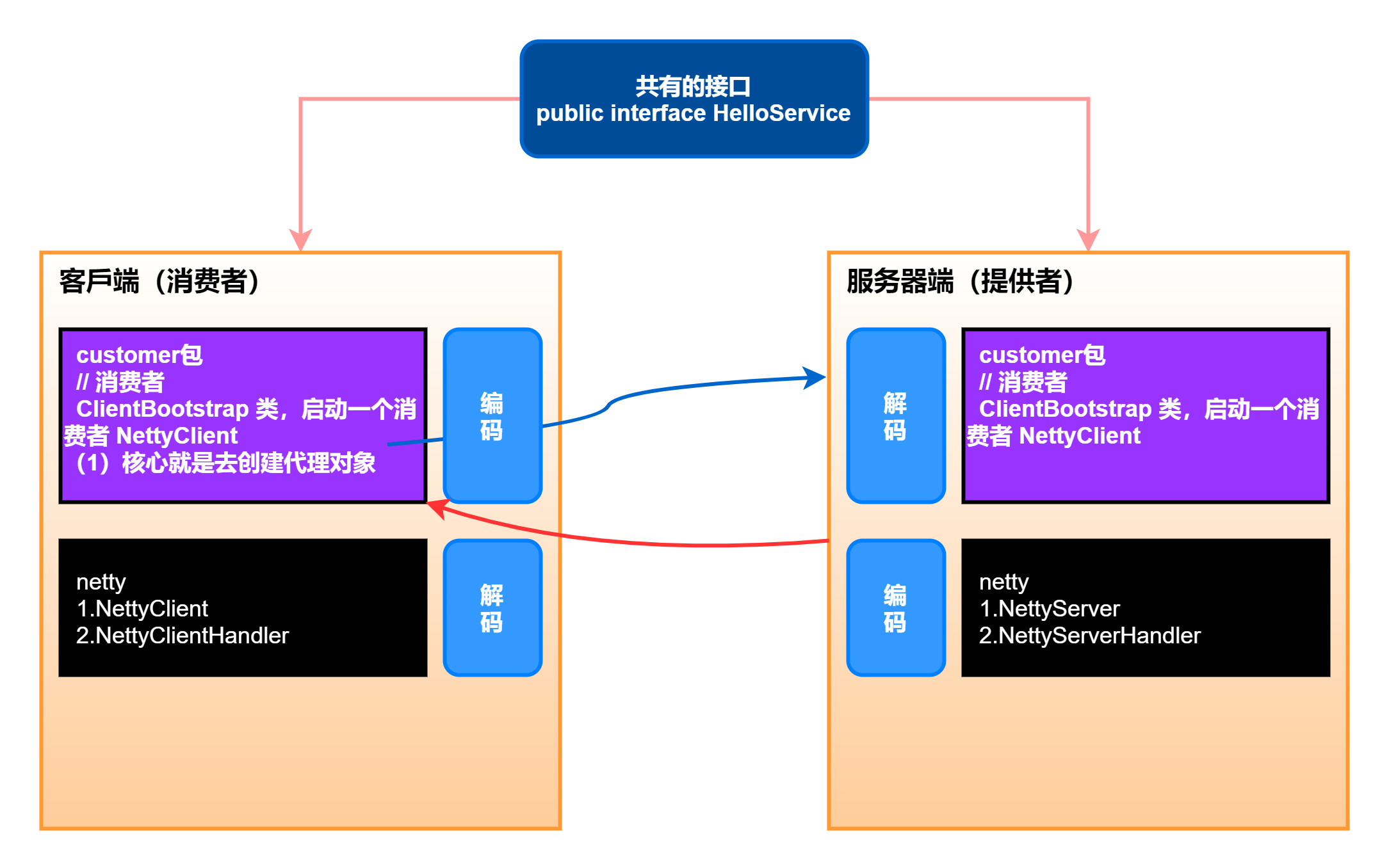
公共接口代码:
public interface HelloService {
String hello(String message);
}
服务提供者代码:
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
private static int count = 0;
// 当有消费方调用该方法时,就返回一个结果
@Override
public String hello(String message) {
System.out.println("收到客户端消息=" + message);
// 根据 message 返回不同的结果
if(message != null){
return "你好,客户端,我已经收到你的消息【" + message + "】第" + (++count) + "次";
}else{
return "你好,客户端,我已经收到你的消息";
}
}
}
/**
* ServerBootstrap 会启动一个服务提供者,就是NettyServer
*/
public class ServerBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NettyServer.startServer("127.0.0.1", 7000);
}
}
服务端代码:
public class NettyServer {
public static void startServer(String hostname, int port){
startServer0(hostname, port);
}
// 编写一个方法,完成对 NettyServer 初始化工作
private static void startServer0(String hostname, int port){
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8);
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(hostname, port).sync();
System.out.println("服务提供方开始提供服务......");
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
// 获取客户端发送的消息,并调用服务
System.out.println("msg=" + msg);
// 客户端在调用服务器的 api 时,需要定义一个协议
// 比如我们要求 每次发消息时都必须以某个字符串开头 ""HelloService#hello#"
if(msg.toString().startsWith("HelloService#hello#")){
String result = new HelloServiceImpl().hello(msg.toString().substring(msg.toString().lastIndexOf("#") + 1));
ctx.writeAndFlush(result);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端代码:
public class NettyClient {
// 创建线程池
private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
private static NettyClientHandler client;
private int count = 0;
// 编写方法使用代理模式,获取一个代理对象
public Object getBean(final Class<?> serviceClass, final String providerName) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{serviceClass},
(proxy, method, args) -> {
System.out.println("(proxy, method, args) 进入....." + (++count) + "次");
// 客户端每调用一次,就会进入到该代码
if (client == null) {
initClient();
}
// 设置要发给服务器端的信息
// providerName 协议头,args[0] 就是客户端调用 api hello(???),参数
client.setPara(providerName + args[0]);
return executor.submit(client).get();
});
}
// 初始化客户端
private static void initClient() {
client = new NettyClientHandler();
// 创建 EventLoopGroup
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(client);
}
});
try {
bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 7000).sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter implements Callable {
// 上下文
private ChannelHandlerContext context;
// 返回的结果
private String result;
// 客户端调用方法时,传入的参数
private String para;
// 与服务器的连接创建成功后,就会被调用
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(" channelActive 被调用");
context = ctx;
}
// 收到服务器的数据后,就会调用此方法
@Override
public synchronized void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(" channelRead 被调用");
result = msg.toString();
// 唤醒等待的线程
notify();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
}
// 被代理对象调用,发送数据给服务器,-> wait ->等待被唤醒 -> 返回结果
@Override
public synchronized Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(" call1 被调用");
context.writeAndFlush(para);
// 进行 wait
// 等待 channelRad 方法获取到服务器的结果后,唤醒
wait();
System.out.println(" call2 被调用");
return result;
}
void setPara(String para){
System.out.println(" setPara 被调用");
this.para = para;
}
}
public class ClientBootstrap {
// 定义协议头
public static final String providerName = "HelloService#hello#";
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 创建一个消费者
NettyClient customer = new NettyClient();
// 创建代理对象
HelloService service = (HelloService) customer.getBean(HelloService.class, providerName);
for (; ; ) {
Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);
// 通过代理对象 调用服务提供者的方法
String res = service.hello("你好 dubbo~~~~");
System.out.println("调用的结果 res =" + res);
}
}
}
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: