1. java中的引用(Reference)
引用是java中堆和栈的桥梁,想要访问堆中的对象,就必须通过引用来访问(8个基本数据类型除外)
在垃圾回收中,如果一个对象仍然被GcRoots引用,那么就不会被回收(强引用),这也不是绝对的,主要是根据引用类型来决定的
在jvm中也有对于的抽象类 Reference
package java.lang.ref;
import jdk.internal.vm.annotation.ForceInline;
import jdk.internal.vm.annotation.IntrinsicCandidate;
import jdk.internal.access.JavaLangRefAccess;
import jdk.internal.access.SharedSecrets;
import jdk.internal.ref.Cleaner;
/**
* Abstract base class for reference objects. This class defines the
* operations common to all reference objects. Because reference objects are
* implemented in close cooperation with the garbage collector, this class may
* not be subclassed directly.
*
* @author Mark Reinhold
* @since 1.2
*/
public abstract class Reference<T> {
...
}
并且软/弱/虚引用分别都有对于的实现类
1.1 引用分类
引用类型主要分为四类,四种引用在垃圾回收时表现不同
1、 强引用不回收;
2、 软引用内存不足时回收;
3、 弱引用发现即回收;
4、 虚引用对象跟踪回收;
由强到虚,回收级别递增.
1.1.1 强引用(StrongReference)
开发过程中的用的基本都是强引用
String str = new String("hello world");
这种最常见的创建对象的方式就是强引用.
这种引用jvm是不会进行回收的,只有当引用被置为null的时候,jvm才会进行回收.
例子证明:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello world");
// 垃圾回收
System.gc();
// 线程休眠3s,等待gc完成
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 如果能打印,就说明没被回收
System.out.print(str);
}
}
一般情况下,出现内存泄漏的问题都是因为强引用.
1.1.2 软引用(SoftReference)
软引用是用来做一些非必要但是还有用的对象. 例如缓存
当内存不足时,软引用会被回收.
具体的逻辑为:
1、 内存空间不足,进行垃圾回收,回收不可达对象;
2、 不可达对象回收后,内存空间依然不足,进行软引用的回收;
3、 如果软引用回收后,内存空间依然不足,报错OOM,如果内存空间足够,则不报OOM;
软引用在jdk中有对应的实现类
package java.lang.ref;
/**
* Soft reference objects, which are cleared at the discretion of the garbage
* collector in response to memory demand. Soft references are most often used
* to implement memory-sensitive caches.
*
* <p> Suppose that the garbage collector determines at a certain point in time
* that an object is <a href="package-summary.html#reachability">softly
* reachable</a>. At that time it may choose to clear atomically all soft
* references to that object and all soft references to any other
* softly-reachable objects from which that object is reachable through a chain
* of strong references. At the same time or at some later time it will
* enqueue those newly-cleared soft references that are registered with
* reference queues.
*
* <p> All soft references to softly-reachable objects are guaranteed to have
* been cleared before the virtual machine throws an
* {@code OutOfMemoryError}. Otherwise no constraints are placed upon the
* time at which a soft reference will be cleared or the order in which a set
* of such references to different objects will be cleared. Virtual machine
* implementations are, however, encouraged to bias against clearing
* recently-created or recently-used soft references.
*
* <p> Direct instances of this class may be used to implement simple caches;
* this class or derived subclasses may also be used in larger data structures
* to implement more sophisticated caches. As long as the referent of a soft
* reference is strongly reachable, that is, is actually in use, the soft
* reference will not be cleared. Thus a sophisticated cache can, for example,
* prevent its most recently used entries from being discarded by keeping
* strong referents to those entries, leaving the remaining entries to be
* discarded at the discretion of the garbage collector.
*
* @author Mark Reinhold
* @since 1.2
*/
public class SoftReference<T> extends Reference<T> {
...
}
我们用一个例子证明软引用在内存不足时会被回收:
import java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
public class SoftReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个软引用 hello_world 关联了一个强引用对象String,当然这个对象创建完就不可达了,会被回收掉,
// 此时我们还能否从软引用中获取该对象?
SoftReference hello_world = new SoftReference(new String("hello world"));
// 确定可以通过软引用获取String
System.out.println(hello_world.get().toString());
// 接下来设置堆内存大小为 -Xms10M -Xmx10M -XX:+PrintGCDetails
// 并触发垃圾回收
// 进行异常捕获,最后输出软引用
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10];
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("垃圾回收后");
System.out.println(hello_world.get());
}
}
}
可以看到结果
垃圾回收前后:
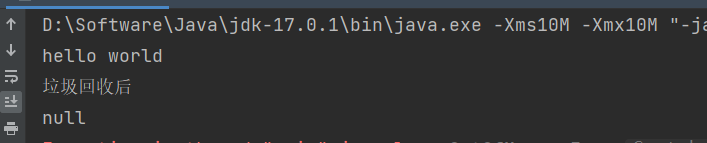
此时可以证明: 当内存不足时,会将软引用回收.
注意: 软引用回收指的是,只被软引用关联的对象,如果一个对象既有弱引用,又有强引用,那么是不会被回收的.
1.1.3 弱引用(WeakReference)
弱引用的回收比软引用要快,每次gc的时候都会回收,当然这里的回收也指的是只有弱引用的对象.
这意味着弱引用的生命周期只有一次垃圾回收的长度.
弱引用也有对应的实现类:
package java.lang.ref;
/**
* Weak reference objects, which do not prevent their referents from being
* made finalizable, finalized, and then reclaimed. Weak references are most
* often used to implement canonicalizing mappings.
*
* <p> Suppose that the garbage collector determines at a certain point in time
* that an object is <a href="package-summary.html#reachability">weakly
* reachable</a>. At that time it will atomically clear all weak references to
* that object and all weak references to any other weakly-reachable objects
* from which that object is reachable through a chain of strong and soft
* references. At the same time it will declare all of the formerly
* weakly-reachable objects to be finalizable. At the same time or at some
* later time it will enqueue those newly-cleared weak references that are
* registered with reference queues.
*
* @author Mark Reinhold
* @since 1.2
*/
public class WeakReference<T> extends Reference<T> {
...
}
弱引用的回收证明例子:
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
public class WeakReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeakReference weakReference =
new WeakReference<>(new String("hello world"));
System.out.println(weakReference.get());
System.gc();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("垃圾回收后");
System.out.println(weakReference.get());
}
}
结果证明:
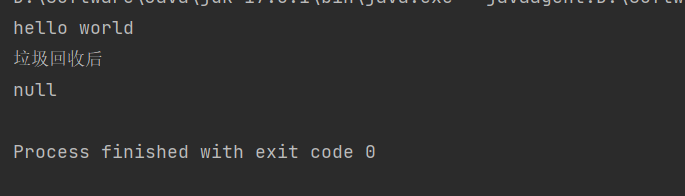
1.1.4 虚引用(PhantomReference)
虚引用相比于软/弱引用来说回收的级别更高,也无法根据虚引用来获取对应的对象
对对象来说,有虚引用和没有虚引用是一样的,对对象的生命周期没有任何影响.
虚引用唯一的作用就是来作为对象回收的跟踪,当对象被回收的时候可以通知程序该对象被回收了,所以虚引用的创建必须要指定一个虚引用队列.
虚引用也有对应的实现类
package java.lang.ref;
import jdk.internal.vm.annotation.IntrinsicCandidate;
/**
* Phantom reference objects, which are enqueued after the collector
* determines that their referents may otherwise be reclaimed. Phantom
* references are most often used to schedule post-mortem cleanup actions.
*
* <p> Suppose the garbage collector determines at a certain point in time
* that an object is <a href="package-summary.html#reachability">
* phantom reachable</a>. At that time it will atomically clear
* all phantom references to that object and all phantom references to
* any other phantom-reachable objects from which that object is reachable.
* At the same time or at some later time it will enqueue those newly-cleared
* phantom references that are registered with reference queues.
*
* <p> In order to ensure that a reclaimable object remains so, the referent of
* a phantom reference may not be retrieved: The {@code get} method of a
* phantom reference always returns {@code null}.
* The {@link #refersTo(Object) refersTo} method can be used to test
* whether some object is the referent of a phantom reference.
*
* @author Mark Reinhold
* @since 1.2
*/
public class PhantomReference<T> extends Reference<T> {
...
}
可以通过代码验证虚引用的对象回收通知功能:
import java.lang.ref.PhantomReference;
import java.lang.ref.Reference;
import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
public class PhantomReferenceTest {
static ReferenceQueue referenceQueue = null;
/**
* 守护线程,监听queue队列,当有虚引用被回收时,就可以看到输出哪个对象被回收了
*/
public static class CheckGcThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
if (referenceQueue != null) {
Reference remove = null;
try {
remove = referenceQueue.remove();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (remove != null) {
System.out.println(remove+"对象被回收了");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动队列监听线程 设置为守护线程,当主线程结束的时候随之结束
CheckGcThread checkGcThread = new CheckGcThread();
checkGcThread.setDaemon(true);
checkGcThread.start();
// 虚引用的创建必须要传入一个队列
referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue();
PhantomReference hello_world = new PhantomReference(new String("hello" +
" world"), referenceQueue);
// 无法通过虚引用获取对象的值
System.out.println(hello_world.get());
// 垃圾回收
System.gc();
}
}
可以看到结果:
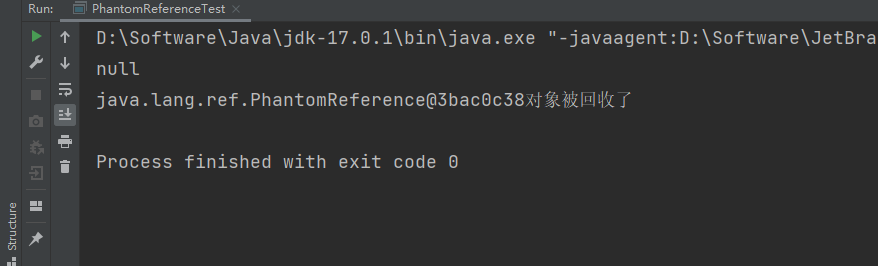
1.2 扩展
终结器引用: 用于调用对象的finalize方法,也是借助于队列的方式,一般情况用不到
对应实现类:
package java.lang.ref;
/**
* Final references, used to implement finalization
*/
class FinalReference<T> extends Reference<T> {
...
}
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: