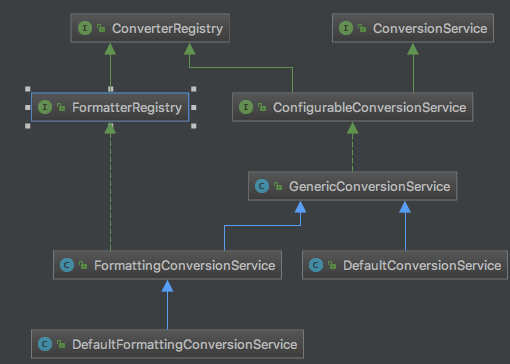
上一篇分析了继承图的右半部分,这次来分析左半部分。
Spring 3为此引入了一个方便的Formatter SPI来直接解决这些问题,这个接口为客户端环境提供一种简单强大并且替代PropertyEditor的方案。
一般来说,当你需要实现通用的类型转换逻辑时请使用Converter SPI,例如,在java.util.Date和java.lang.Long之间进行转换。当你在一个客户端环境(比如web应用程序)工作并且需要解析和打印本地化的字段值时,请使用Formatter SPI。ConversionService接口为这两者提供了一套统一的类型转换API。
public interface Formatter<T> extends Printer<T>, Parser<T> {}
public interface Printer<T> {
String print(T object, Locale locale);
}
public interface Parser<T> {
T parse(String clientValue, Locale locale) throws ParseException;
}
实现print()操作可以将类型T的实例按客户端区域设置的显示方式打印出来。实现parse()操作可以从依据客户端区域设置返回的格式化表示中解析出类型T的实例。如果解析尝试失败,你的格式化器应该抛出一个ParseException或者IllegalArgumentException。请注意确保你的格式化器实现是线程安全的。
DateFormatter作为Formatter实现的一个例子:
package org.springframework.format.datetime;
public final class DateFormatter implements Formatter<Date> {
private String pattern;
public DateFormatter(String pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
}
public String print(Date date, Locale locale) {
if (date == null) {
return "";
}
return getDateFormat(locale).format(date);
}
public Date parse(String formatted, Locale locale) throws ParseException {
if (formatted.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
return getDateFormat(locale).parse(formatted);
}
protected DateFormat getDateFormat(Locale locale) {
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(this.pattern, locale);
dateFormat.setLenient(false);
return dateFormat;
}
}
字段格式化可以通过字段类型或者注解进行配置,要将一个注解绑定到一个格式化器,可以实现AnnotationFormatterFactory:
package org.springframework.format;
public interface AnnotationFormatterFactory<A extends Annotation> {
Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes();
Printer<?> getPrinter(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);
Parser<?> getParser(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);
}
泛型参数A代表你想要关联格式化逻辑的字段注解类型,例如org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat。让getFieldTypes()方法返回可能使用注解的字段类型,让getPrinter()方法返回一个可以打印被注解字段的值的打印机(Printer),让getParser()方法返回一个可以解析被注解字段的客户端值的解析器(Parser)。
下面这个AnnotationFormatterFactory实现的示例把@NumberFormat注解绑定到一个格式化器,此注解允许指定数字样式或模式:
public class NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory extends EmbeddedValueResolutionSupport
implements AnnotationFormatterFactory<NumberFormat> {
@Override
public Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {
return NumberUtils.STANDARD_NUMBER_TYPES;
}
@Override
public Printer<Number> getPrinter(NumberFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return configureFormatterFrom(annotation);
}
@Override
public Parser<Number> getParser(NumberFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return configureFormatterFrom(annotation);
}
private Formatter<Number> configureFormatterFrom(NumberFormat annotation) {
String pattern = resolveEmbeddedValue(annotation.pattern());
if (StringUtils.hasLength(pattern)) {
return new NumberStyleFormatter(pattern);
}
else {
Style style = annotation.style();
if (style == Style.CURRENCY) {
return new CurrencyStyleFormatter();
}
else if (style == Style.PERCENT) {
return new PercentStyleFormatter();
}
else {
return new NumberStyleFormatter();
}
}
}
}
FormatterRegistry是一个用于注册格式化器和转换器的服务提供接口(SPI)。FormattingConversionService是一个适用于大多数环境的FormatterRegistry实现,可以以编程方式或利用FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean声明成Spring bean的方式来进行配置。由于它也实现了ConversionService,所以可以直接配置它与Spring的DataBinder以及Spring表达式语言(SpEL)一起使用。
public interface FormatterRegistry extends ConverterRegistry {
void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, Parser<?> parser);
void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter);
void addFormatterForFieldType(Formatter<?> formatter);
void addFormatterForAnnotation(AnnotationFormatterFactory<?, ?> factory);
}
FormatterRegistrar是一个通过FormatterRegistry注册格式化器和转换器的服务提供接口(SPI),当要为一个给定的格式化类别(比如时间格式化)注册多个关联的转换器和格式化器时,FormatterRegistrar会非常有用。
public interface FormatterRegistrar {
void registerFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry);
}
接下来看一下FormatterRegistry的实现类FormattingConversionService。
@Override
public void addFormatter(Formatter<?> formatter) {
addFormatterForFieldType(getFieldType(formatter), formatter);
}
@Override
public void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter) {
addConverter(new PrinterConverter(fieldType, formatter, this));
addConverter(new ParserConverter(fieldType, formatter, this));
}
@Override
public void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, Parser<?> parser) {
addConverter(new PrinterConverter(fieldType, printer, this));
addConverter(new ParserConverter(fieldType, parser, this));
}
@Override
public void addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(AnnotationFormatterFactory<? extends Annotation> annotationFormatterFactory) {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = getAnnotationType(annotationFormatterFactory);
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null && annotationFormatterFactory instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) annotationFormatterFactory).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes = annotationFormatterFactory.getFieldTypes();
for (Class<?> fieldType : fieldTypes) {
addConverter(new AnnotationPrinterConverter(annotationType, annotationFormatterFactory, fieldType));
addConverter(new AnnotationParserConverter(annotationType, annotationFormatterFactory, fieldType));
}
}
四个addFormatter()方法,最终目的都是调用 addConverter()方法新增两个转换器,PrinterConverter是将fieldType转换为String的转换器,ParserConverter是将String转换为fieldType的转换器,注解形式的分别为AnnotationPrinterConverter和AnnotationParserConverter。这四个接口都是GenericConverter的实现类,需要实现自己的getConvertibleTypes()方法和convert()方法。
private static class PrinterConverter implements GenericConverter {
private final Class<?> fieldType;
private final TypeDescriptor printerObjectType;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private final Printer printer;
private final ConversionService conversionService;
public PrinterConverter(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, ConversionService conversionService) {
this.fieldType = fieldType;
this.printerObjectType = TypeDescriptor.valueOf(resolvePrinterObjectType(printer));
this.printer = printer;
this.conversionService = conversionService;
}
@Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(this.fieldType, String.class));
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
if (!sourceType.isAssignableTo(this.printerObjectType)) {
source = this.conversionService.convert(source, sourceType, this.printerObjectType);
}
if (source == null) {
return "";
}
return this.printer.print(source, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
}
@Nullable
private Class<?> resolvePrinterObjectType(Printer<?> printer) {
return GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(printer.getClass(), Printer.class);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (this.fieldType.getName() + " -> " + String.class.getName() + " : " + this.printer);
}
}
getConvertibleTypes()方法可以看出是fieldType到String的转换,convert()方法是具体转换逻辑,内部使用Printer来格式化fieldType的。具体是先判断printerObjectType是否为sourceType类型,printerObjectType为Printer的泛型类型通过GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument()得出的。若printerObjectType不是sourceType类型,则使用conversionService将source转换为printerObjectType,在使用printer对象格式化。ParserConverter做了个逆向转化不再说了。
@Nullable
public static Class<?> resolveTypeArgument(Class<?> clazz, Class<?> genericIfc) {
ResolvableType resolvableType = ResolvableType.forClass(clazz).as(genericIfc);
if (!resolvableType.hasGenerics()) {
return null;
}
return getSingleGeneric(resolvableType);
}
@Nullable
private static Class<?> getSingleGeneric(ResolvableType resolvableType) {
Assert.isTrue(resolvableType.getGenerics().length == 1,
() -> "Expected 1 type argument on generic interface [" + resolvableType +
"] but found " + resolvableType.getGenerics().length);
return resolvableType.getGeneric().resolve();
}
下面看分析一下AnnotationPrinterConverter。
private class AnnotationParserConverter implements ConditionalGenericConverter {
private final Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private final AnnotationFormatterFactory annotationFormatterFactory;
private final Class<?> fieldType;
public AnnotationParserConverter(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType,
AnnotationFormatterFactory<?> annotationFormatterFactory, Class<?> fieldType) {
this.annotationType = annotationType;
this.annotationFormatterFactory = annotationFormatterFactory;
this.fieldType = fieldType;
}
@Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(String.class, fieldType));
}
@Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
return targetType.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
Annotation ann = targetType.getAnnotation(this.annotationType);
if (ann == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Expected [" + this.annotationType.getName() + "] to be present on " + targetType);
}
AnnotationConverterKey converterKey = new AnnotationConverterKey(ann, targetType.getObjectType());
GenericConverter converter = cachedParsers.get(converterKey);
if (converter == null) {
Parser<?> parser = this.annotationFormatterFactory.getParser(
converterKey.getAnnotation(), converterKey.getFieldType());
converter = new ParserConverter(this.fieldType, parser, FormattingConversionService.this);
cachedParsers.put(converterKey, converter);
}
return converter.convert(source, sourceType, targetType);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (String.class.getName() + " -> @" + this.annotationType.getName() + " " +
this.fieldType.getName() + ": " + this.annotationFormatterFactory);
}
}
与PrinterConverter不同,它实现了ConditionalGenericConverter,所以需要实现matches()方法,这个方法返回值是源类型上是否有该AnnotationFormatterFactory的泛型注解类型,这样一个AnnotationFormatterFactory只能处理有且只有一种注解类型。convert()方法就是首先调用annotationFormatterFactory.getPrinter()得到Printer对象后包装成PrinterConverter,调用其convert()方法完成格式化。
那么客户端是如何使用FormattingConversionService完成字段的格式化的呢,下面给出一个Spring以注解格式化的例子。
*
@Test
public void formatFieldForAnnotation() throws Exception {
formattingService.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new JodaDateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());
doTestFormatFieldForAnnotation(Model.class, false);
}
*
public static class Model {
@org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat(style="S-")
public Date date;
@org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat(pattern="M-d-yy")
public List<Date> dates;
public List<Date> getDates() {
return dates;
}
public void setDates(List<Date> dates) {
this.dates = dates;
}
}
private void doTestFormatFieldForAnnotation(Class<?> modelClass, boolean directFieldAccess) throws Exception {
formattingService.addConverter(new Converter<Date, Long>() {
@Override
public Long convert(Date source) {
return source.getTime();
}
});
formattingService.addConverter(new Converter<DateTime, Date>() {
@Override
public Date convert(DateTime source) {
return source.toDate();
}
});
String formatted = (String) formattingService.convert(new LocalDate(2009, 10, 31).toDateTimeAtCurrentTime()
.toDate(), new TypeDescriptor(modelClass.getField("date")), TypeDescriptor.valueOf(String.class));
assertEquals("10/31/09", formatted);
}
与GenericConversionService一样,FormattingConversionService默认没有任何转换器,并且也没有格式化器,一种是我们调用addFormatter()方法加入自定义格式化器,或者使用它的子类DefaultFormattingConversionService。
public DefaultFormattingConversionService(
@Nullable StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver, boolean registerDefaultFormatters) {
if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {
setEmbeddedValueResolver(embeddedValueResolver);
}
DefaultConversionService.addDefaultConverters(this);
if (registerDefaultFormatters) {
addDefaultFormatters(this);
}
}
使用DefaultConversionService.addDefaultConverters(this)加入了Spring为我们写好的转化器,addDefaultFormatters()方法使用多个FormatterRegistrar往formatterRegistry批量注册了多个格式化器,当Spring默认的格式化器不能满足我们的需求时,我们可以实现我们自己的FormatterRegistrar批量注册格式化器。
public static void addDefaultFormatters(FormatterRegistry formatterRegistry) {
// Default handling of number values
formatterRegistry.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());
// Default handling of monetary values
if (jsr354Present) {
formatterRegistry.addFormatter(new CurrencyUnitFormatter());
formatterRegistry.addFormatter(new MonetaryAmountFormatter());
formatterRegistry.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new Jsr354NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());
}
// Default handling of date-time values
// just handling JSR-310 specific date and time types
new DateTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);
if (jodaTimePresent) {
// handles Joda-specific types as well as Date, Calendar, Long
new JodaTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);
}
else {
// regular DateFormat-based Date, Calendar, Long converters
new DateFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);
}
}
Spring提供了一个FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean方便使用XML配置FormattingConversionService。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService(this.embeddedValueResolver, this.registerDefaultFormatters);
ConversionServiceFactory.registerConverters(this.converters, this.conversionService);
registerFormatters(this.conversionService);
}
private void registerFormatters(FormattingConversionService conversionService) {
if (this.formatters != null) {
for (Object formatter : this.formatters) {
if (formatter instanceof Formatter<?>) {
conversionService.addFormatter((Formatter<?>) formatter);
}
else if (formatter instanceof AnnotationFormatterFactory<?>) {
conversionService.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation((AnnotationFormatterFactory<?>) formatter);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Custom formatters must be implementations of Formatter or AnnotationFormatterFactory");
}
}
}
if (this.formatterRegistrars != null) {
for (FormatterRegistrar registrar : this.formatterRegistrars) {
registrar.registerFormatters(conversionService);
}
}
}
formatters和formatterRegistrars用来扩展格式化器。