JAVA并发编程(十五)LongAccumulator类原理探究
- JAVA并发编程(十五)LongAccumulator类原理探究
-
- 1.1简单介绍LongAccumulator
- 1.2 LongAccumulator源码分析
JAVA并发编程(十五)LongAccumulator类原理探究
1.1简单介绍LongAccumulator
上一篇博客讲到了LongAdder这个类他弥补了AtomicLong在多线程下的不足,但是问题又来了。LongAdder这个类只能做一些简单的加减操作,一些复杂的运算,却又没有办法了。这个时候,我们的LongAccumulator就出现了。
LongAccumulator可以进行自定义两个数的运算规则,所以也包括加减操作,换而言之LongAdder类其实是LongAccumulator的一个特例。我们来看看他的类图:
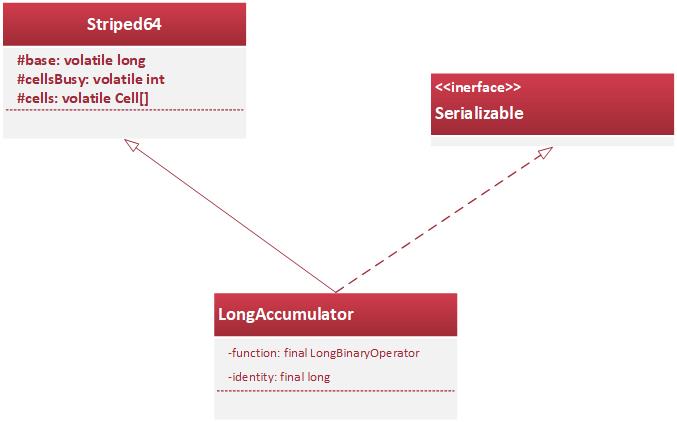
LongAccumulator类内部维护两个变量,function其实是双目运算器的接口,他根据输入的两个参数,返回一个计算值(由传入的两个参数计算得到),而identity其实是LongAccumulator的初始值。
1.2 LongAccumulator源码分析
上面讲了那么多,我么了先来看看他的有参构造器和他的双目运算接口的源码:
public LongAccumulator(LongBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction,
long identity) {
this.function = accumulatorFunction;
//把传进来的初始值
base = this.identity = identity;
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface LongBinaryOperator {
/**
* Applies this operator to the given operands.
*
* @param left the first operand
* @param right the second operand
* @return the operator result
*/
long applyAsLong(long left, long right);
}
我们看到了源码后,其实很容易理解,LongBinaryOperator这个接口其实是帮我们定义运算规则的,所以我们只要实现这个接口把运算规则定义为两数相加,就可以把LongAccumulator变成LongAdder了。代码如下:
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator(new LongBinaryOperator() {
@Override
public long applyAsLong(long left, long right) {
return left+right;
}
}, 0);
如上代码,我们直接实现该接口,然后在applyAsLong方法里面定义运算规则,然后初始值给个0,你会发现这不就是我们的LongAdder。而且,我们初始值可以给非0的数字,但是LongAdder却不可以,而且我还可以修改上面的运算规则,让两数相乘也是可以的,是不是感觉LongAccumulator的功能更加强大。其实两个类最大不同,我们可以从源码上看出来的(如下):
//这个是LongAccumulator的accumulate方法
public void accumulate(long x) {
Cell[] as; long b, v, r; int m; Cell a;
if ((as = cells) != null ||
(r = function.applyAsLong(b = base, x)) != b && !casBase(b, r)) {
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
(r = function.applyAsLong(v = a.value, x)) == v ||
a.cas(v, r)))
longAccumulate(x, function, uncontended);
}
}
//这个是LongAdder的add方法
public void add(long x) {
Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a;
if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x)))
longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended);
}
}
从上面代码我们可以看出来,其实LongAccumulator和LongAdder不同就在于,调用caseBase时,LongAdder传递的是b+x,而LongAccumulator传递的是function.applyAsLong(b = base, x),另外在调用longAccumulate的时候,LongAdder传递的是null,而LongAccumulator传递的是function。那么传递function进去会进行怎样的运算呢?
else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x :
fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))
break;
当我们longAccumulate传的空,这个时候就会进行v+x操作,也就是LongAdder,longAccumulate传递的function,他就会按照function的运算规则进行运算。
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: