作者:朱小厮 | 出自:https://hiddenpps.blog.csdn.net/column/info/14800
AMQCommand是用来处理AMQ命令的,其包含了Method, Content Heaeder和Content Body.
下面是通过wireshark抓包的AMQP协议
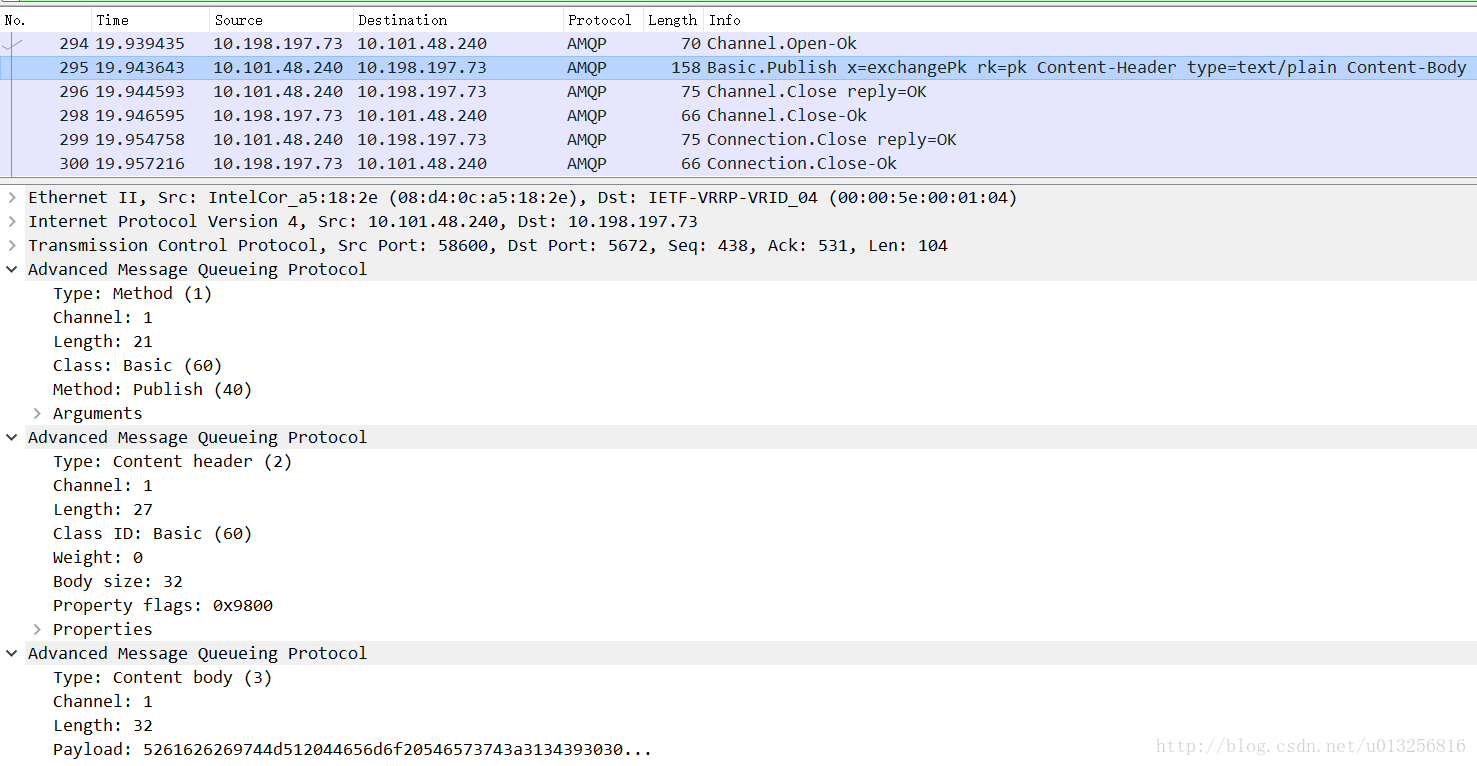
上图中的Basic.Publish命令就包含Method, Content header以及Content body。
AMQCommand不是直接包含Method等成员变量的,而是通过CommandAssembler又做了一次封装。
接下来先看下CommandAssembler类。此类中有这些成员变量:
/** Current state, used to decide how to handle each incoming frame. */
private enum CAState {
EXPECTING_METHOD, EXPECTING_CONTENT_HEADER, EXPECTING_CONTENT_BODY, COMPLETE
private CAState state;
/** The method for this command */
private Method method;
/** The content header for this command */
private AMQContentHeader contentHeader;
/** The fragments of this command's content body - a list of byte[] */
private final List
bodyN;
/** sum of the lengths of all fragments */
private int bodyLength;
/** No bytes of content body not yet accumulated */
private long remainingBodyBytes;
- CAState state标识这此Command目前的状态,是准备处理Method(EXPECTING_METHOD),还是处理Content header(EXPECTING_CONTENT_HEADER),还是准备处理Content body(EXPECTING_CONTENT_BODY),还是以及完成了(COMPLETE)。
- Method method代表type=Method的AMQP帧
- AMQContentHeader contentHeader代表type=Content header的AMQP帧
- final List bodyN代表type=Content body的AMQP帧,就是真正的消息体(Message body)。
- bodyLength就是消息体大小
这个类中除了构造函数,getMethod, getContentHeader, getContentBody,isComplete这个几个方法,最关键的方法就是:
public synchronized boolean handleFrame(Frame f) throws IOException
switch (this.state) {
case EXPECTING_METHOD: consumeMethodFrame(f); break;
case EXPECTING_CONTENT_HEADER: consumeHeaderFrame(f); break;
case EXPECTING_CONTENT_BODY: consumeBodyFrame(f); break;
default:
throw new AssertionError("Bad Command State " + this.state);
}
return isComplete();
这个方法主要是处理AQMP帧的,根据CAState state来处理相应状态类型的帧,然后赋值给相应的成员变量。
采用consumeMethodFrame(Frame f)方法举个例子:
private void consumeMethodFrame(Frame f) throws IOException {
if (f.type == AMQP.FRAME_METHOD) {
this.method = AMQImpl.readMethodFrom(f.getInputStream());
this.state = this.method.hasContent() ? CAState.EXPECTING_CONTENT_HEADER : CAState.COMPLETE;
} else {
throw new UnexpectedFrameError(f, AMQP.FRAME_METHOD);
}
这个方法首先判断当前帧是否是Method帧(AMQP.FRAME_METHOD),然后调用AMQPImp.readMethodFrom的方法。就那Connection.Start这个真来将,它会从socket的输入流中读取:
public Start(MethodArgumentReader rdr) throws IOException {
this(rdr.readOctet(), rdr.readOctet(), rdr.readTable(), rdr.readLongstr(), rdr.readLongstr());
对应于下图:
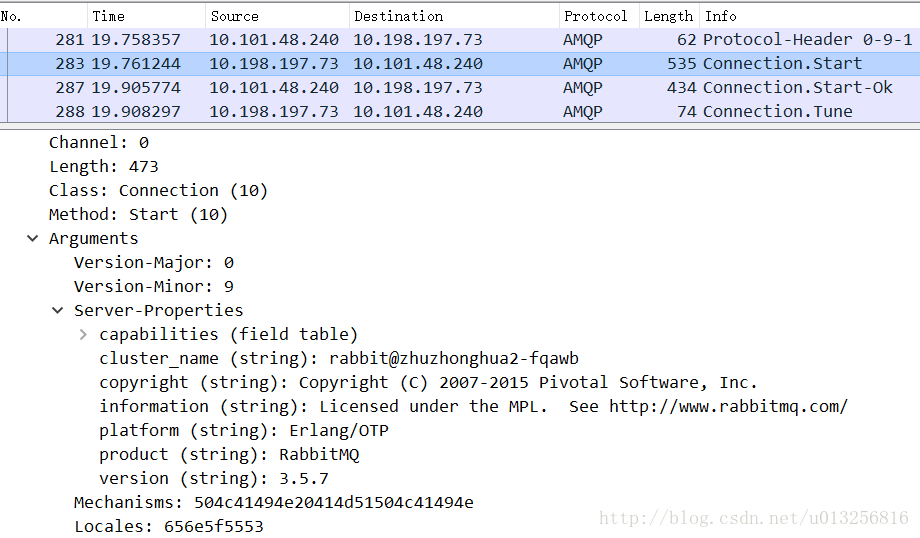
- 第一个rdr.readOctet()是指Version-Magor:0
- 第二个rdr.readOctet()是指Version-Minor:9
- 第三个rdr.readTable()是指Server-Properties
- 第四个rdr.readLongstr()是指Mechanisms
- 第五个rdr.readLongstr()是指Locales
而MethodArgumentReader.readOctet()就是:
public final int readOctet()
throws IOException
clearBits();
return in.readOctet();//in对象是DataInputStream对象
写到这里,思路再跳回来,知道了底层其实是Socket的DataInputStream,其上只是做了封装再封装
CommandAssembler 中的handleFrame这个方法只在AMQCommand中的:
private final CommandAssembler assembler;
public boolean handleFrame(Frame f) throws IOException {
return this.assembler.handleFrame(f);
只在这个方法中调用。CommandAssembler只是对Method,Content-Header,Content-Body做了一下封装。下面继续回到AMQCommand这个类中来。
仔细阅读源码的同学会发现在handleFrame方法当遇到类似Basic.Publish时会有Method,Content-Header,Content-Body一起的报文,那么handleFrame处理完Method之后就直接返回了,没有完全处理完,这该如何是好?
这个就又要联系到AMQConnection中的MainLoop的内部类了。此类中的关键代码如下:
while (_running) {
Frame frame = _frameHandler.readFrame();
if (frame != null) {
_missedHeartbeats = 0;
if (frame.type == AMQP.FRAME_HEARTBEAT) {
// Ignore it: we've already just reset the heartbeat counter.
} else {
if (frame.channel == 0) { // the special channel
_channel0.handleFrame(frame);
} else {
if (isOpen()) {
// If we're still _running, but not isOpen(), then we
// must be quiescing, which means any inbound frames
// for non-zero channels (and any inbound commands on
// channel zero that aren't Connection.CloseOk) must
// be discarded.
ChannelManager cm = _channelManager;
if (cm != null) {
cm.getChannel(frame.channel).handleFrame(frame);
}
}
}
}
} else {
// Socket timeout waiting for a frame.
// Maybe missed heartbeat.
handleSocketTimeout();
}
可以看到这是一个一直轮询读取Frame并处理Frame的过程。在遇到类似Basic.Publish这种带Method, Content-Header, Content-Body的类型的报文时,会循环处理,直到处理完成。注意这里的Method, Content-Header以及Content-Body都是看成单个Frame的,也就是这个while循环要三次,而不是将Basic.Publish看成一个帧。
上面调用的handleFrame方法是AMQChannel类中的(详细可以参考([[五]RabbitMQ-客户端源码之AMQChannel][RabbitMQ-_AMQChannel])):
public void handleFrame(Frame frame) throws IOException {
AMQCommand command = _command;
if (command.handleFrame(frame)) { // a complete command has rolled off the assembly line
_command = new AMQCommand(); // prepare for the next one
handleCompleteInboundCommand(command);
}
可以看到只有当AMQCommand的handleFrame方法返回true时,即执行完成之后才会继续处理。
AMQCommand也有getMethod, getContentHeader, getContentBody等方法,这些都是间接调用CommandAssembler类中相应的方法的。
AMQCommand中也有个特别重要的方法:
/**
* Sends this command down the named channel on the channel's
* connection, possibly in multiple frames.
* @param channel the channel on which to transmit the command
* @throws IOException if an error is encountered
*/
public void transmit(AMQChannel channel) throws IOException {
int channelNumber = channel.getChannelNumber();
AMQConnection connection = channel.getConnection();
synchronized (assembler) {
Method m = this.assembler.getMethod();
connection.writeFrame(m.toFrame(channelNumber));
if (m.hasContent()) {
byte[] body = this.assembler.getContentBody();
connection.writeFrame(this.assembler.getContentHeader()
.toFrame(channelNumber, body.length));
int frameMax = connection.getFrameMax();
int bodyPayloadMax = (frameMax == 0) ? body.length : frameMax
- EMPTY_FRAME_SIZE;
for (int offset = 0; offset < body.length; offset += bodyPayloadMax) {
int remaining = body.length - offset;
int fragmentLength = (remaining < bodyPayloadMax) ? remaining
: bodyPayloadMax;
Frame frame = Frame.fromBodyFragment(channelNumber, body,
offset, fragmentLength);
connection.writeFrame(frame);
}
}
}
connection.flush();
这段主要通过传输AMQP帧的,通过AMQChannel获取到通信链路connection,然后将AMQCommand对象自身的method成员变量(或者包括content-header以及content-body)传送给broker。这段方法里还有判断payload大小是否超过broker端所设置的最大帧大小frameMax,即(frameMax == 0) ? body.length : frameMax - EMPTY_FRAME_SIZE这段代码。当frameMax=0时则没有大小限制,当frameMax不为0时则按照payload拆分成若干的payload然后发送多个FRAME_BODY帧。